Lifecycle management is a feature that helps you manage an asset throughout its entire lifecycle, from creation to archive. It allows you to better monitor an asset's development, implementation, and usage, helping you to ensure compliance and safety.
Asset statuses as a representation of lifecycle stages
All assets are created with a certain asset status, for example Candidate, which indicates the condition of the asset. By enabling the Lifecycle management feature, you're opting to use asset statuses to represent and reflect the lifecycle stages in which an asset can exist at any point in time.
With the help of various tools and features, such as the Lifecycle tracker and lifecycle activities, you determine and manually control the lifecycle stage of an asset, and the status of the asset is automatically updated to match.
Enable or disable Lifecycle management for an asset type
The Lifecycle management feature is currently available for the following asset types:
- AI Agent
- AI Use Case
- Deployed AI Model
- Foundational AI Model
Tip If the feature is available for an asset type, the Activate Lifecycle tracker option is shown in the Lifecycle tab of the asset type's global assignment.
Prerequisites
- You have a global role with the Product Rights > System administration global permission.
Steps
-
On the main toolbar, click
→
Settings.
The Settings page opens. - Click the Operating Model tab.
Operating Model settings are shown. - In the Asset types table, click the relevant asset type.
The asset type overview page opens. - In the tab pane, expand the Global Assignment tab (or the tab of the relevant assignment), and then click Lifecycle.Note If only the Global Assignment tab is shown, it means no one in your organization has added another assignment. In this case, use the Global Assignment. For more information on assignments and scopes, go to Create scoped assignments for the AI Governance asset types.The Lifecycle page opens.
- Select (to enable) or clear (to disable) the Activate Lifecycle tracker option.
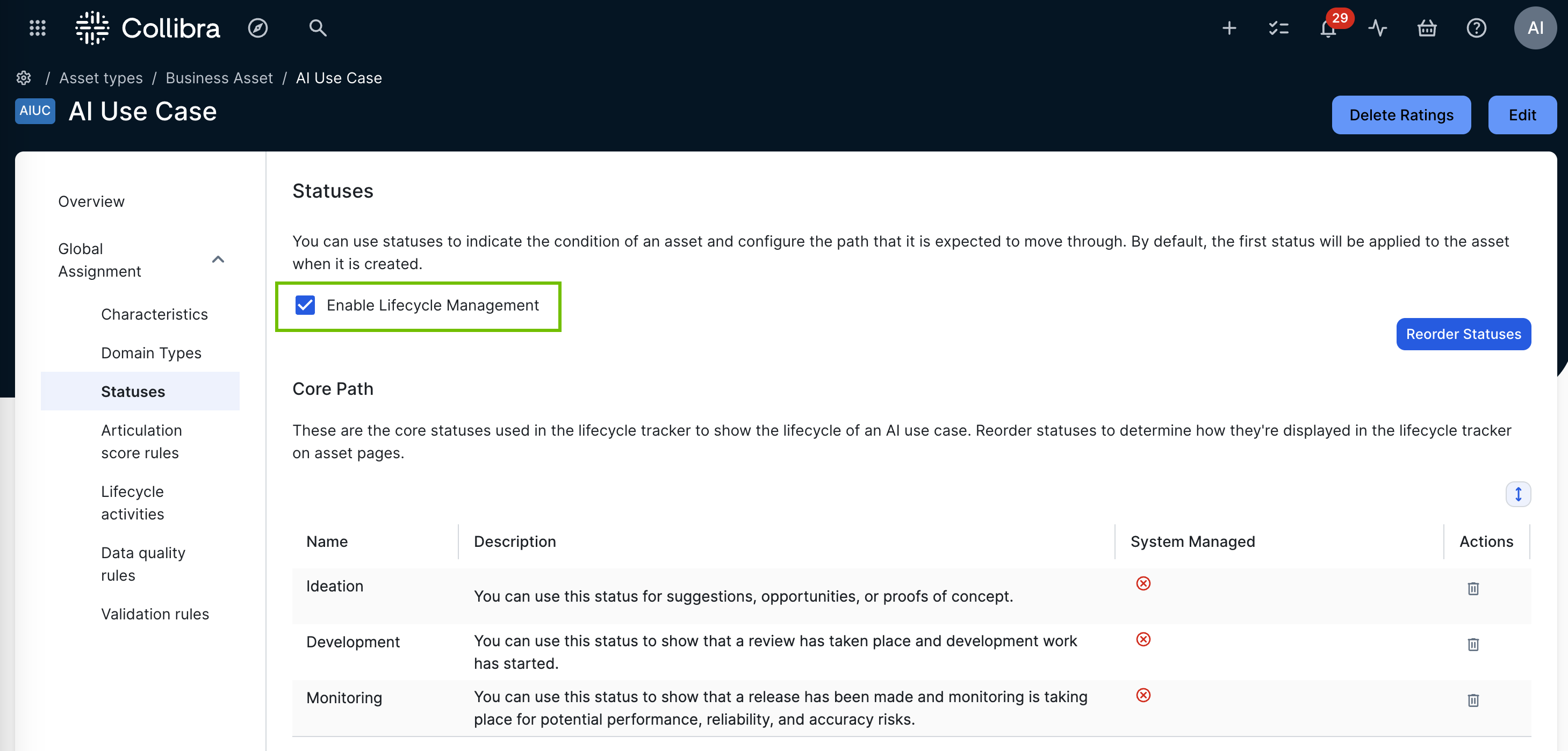
- Click Save.
Configuring lifecycle stages
When configuring the lifecycle stages, there are two tabs to consider: Core phase and Retirement phase.
For guidance on how to configure lifecycle stages, go to Configure the lifecycle stages of AI Governance assets.
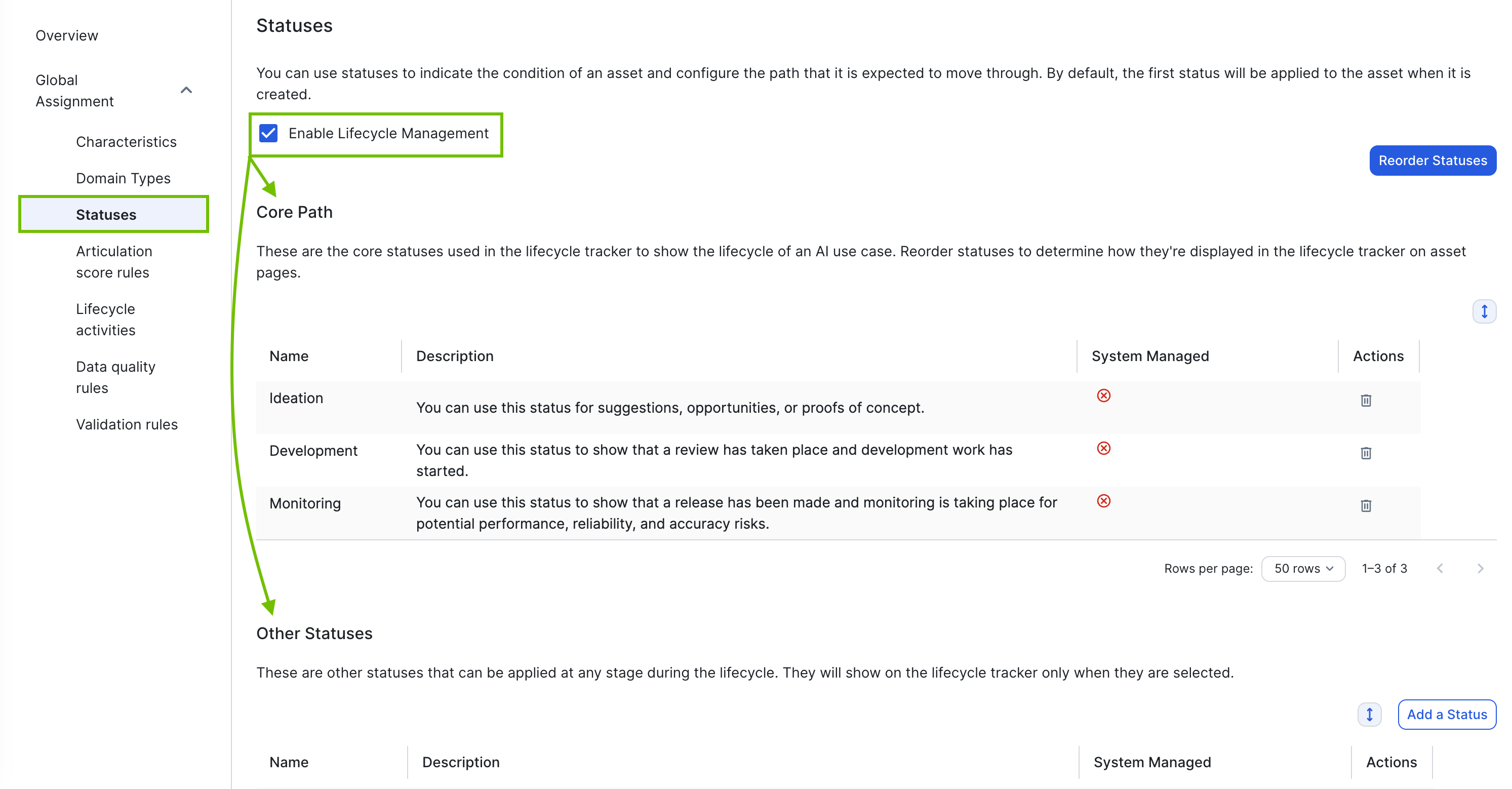
Core phase
Asset statuses included in the Core phase tab represent the active lifecycle stages of an asset. The first asset status listed in the core phase — Ideation, in the example image above— determines the initial status of all newly created assets of this type.
The asset statuses included in the core phase — Ideation, Development, and Monitoring, in this example — are reflected on some product pages, for example on the AI Governance Overview page, and in the Lifecycle tracker.
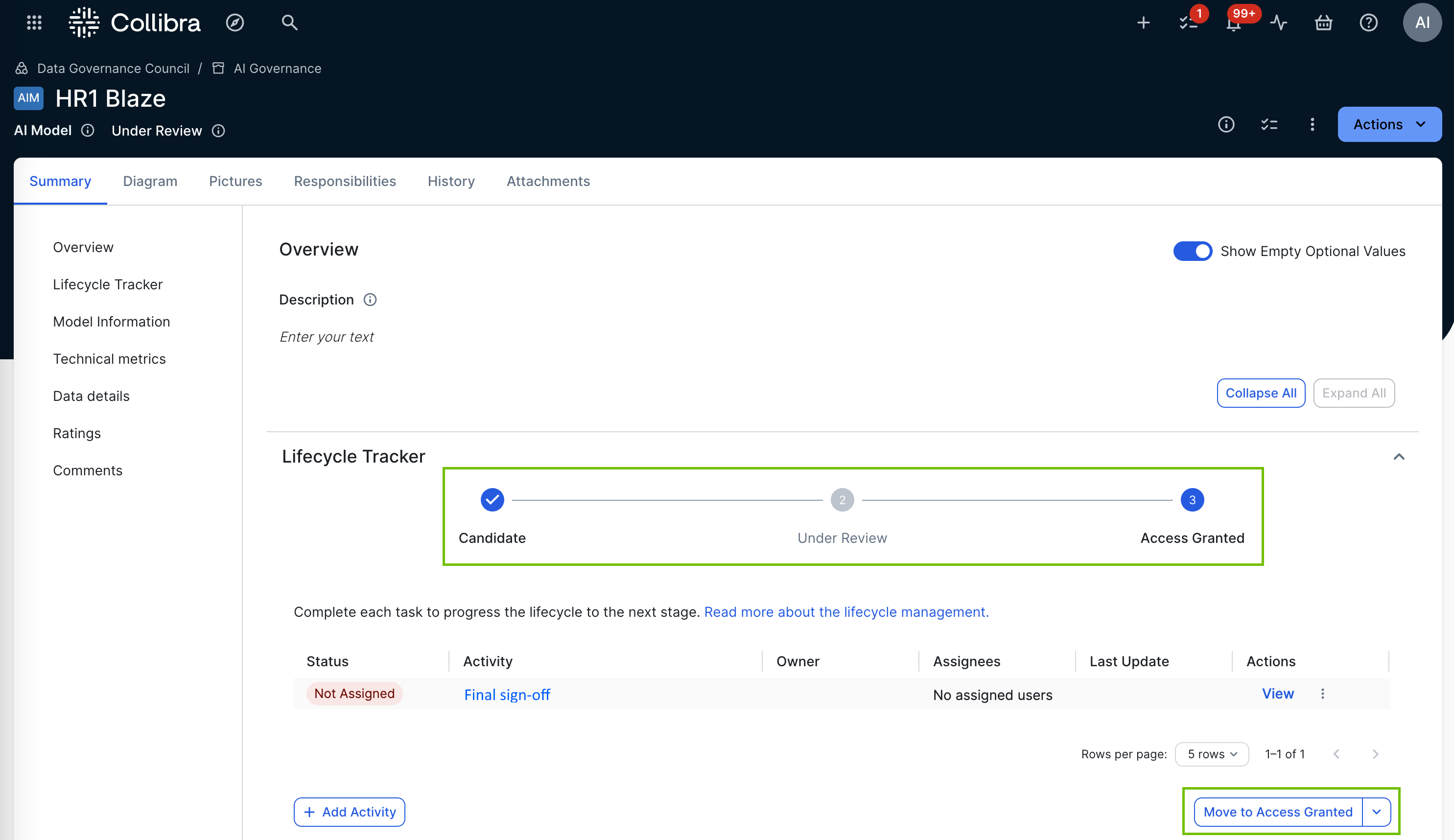
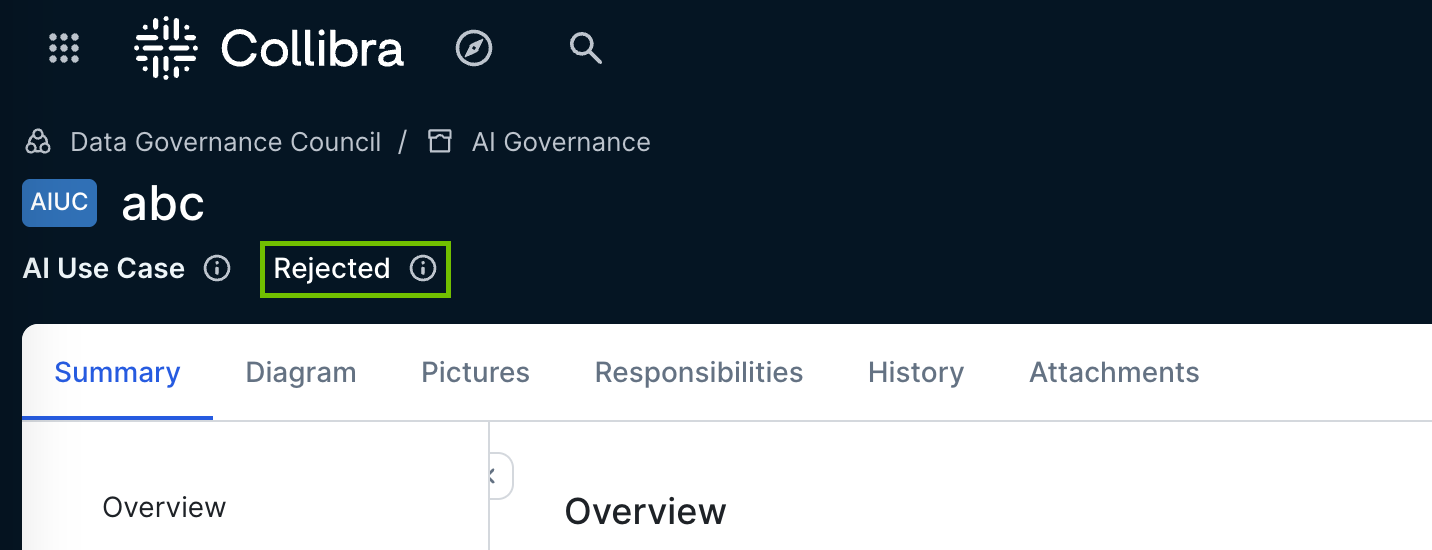
The following image shows the default core phase statuses of the AI Use Case asset type, as reflected in the Lifecycle tracker on an asset page.
![]()
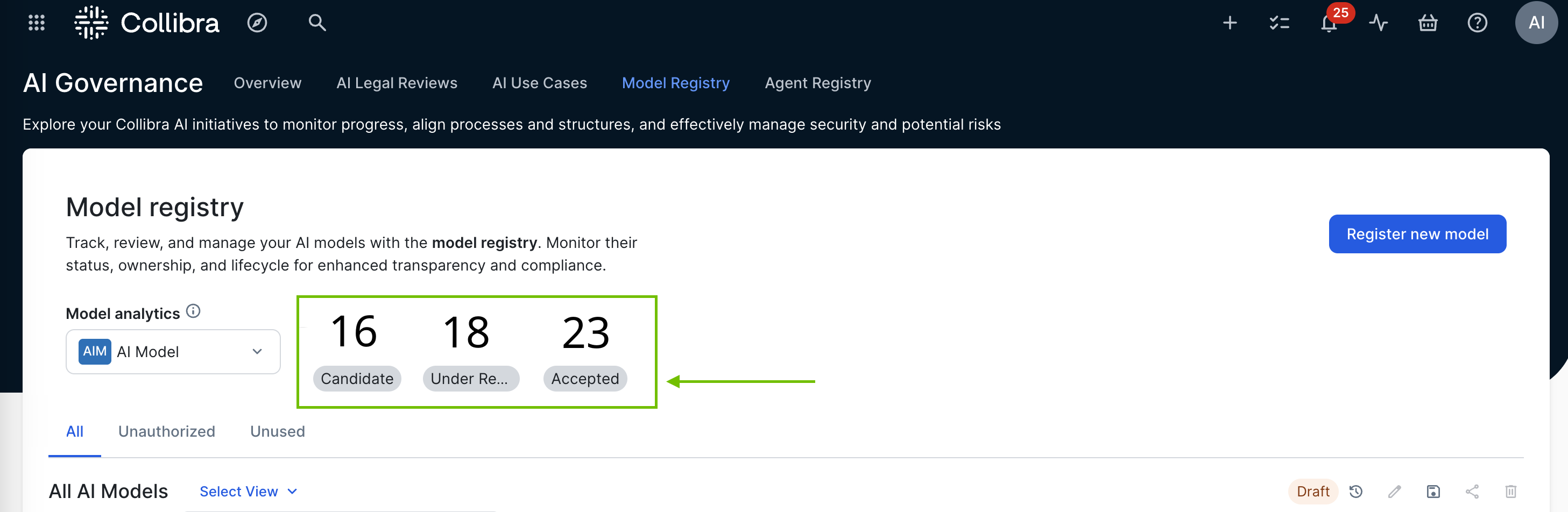
The following image shows the default core statuses of the Deployed AI Model asset type, as reflected in the Model Analytics widget that is included on the AI Governance Model Registry and Agent Registry pages.
Retirement phase
Asset statuses included in the Retirement phase tab represent the inactive lifecycle stages of an asset. For the AI Use Case asset type, the default statuses are Rejected and Archived. They are considered part of the asset lifecycle, but they are not reflected in the Lifecycle tracker or in the Model Analytics widget.
For all assets, regardless of type or status, these statuses are shown below the asset name on asset pages and in asset views that include the Status attribute type.
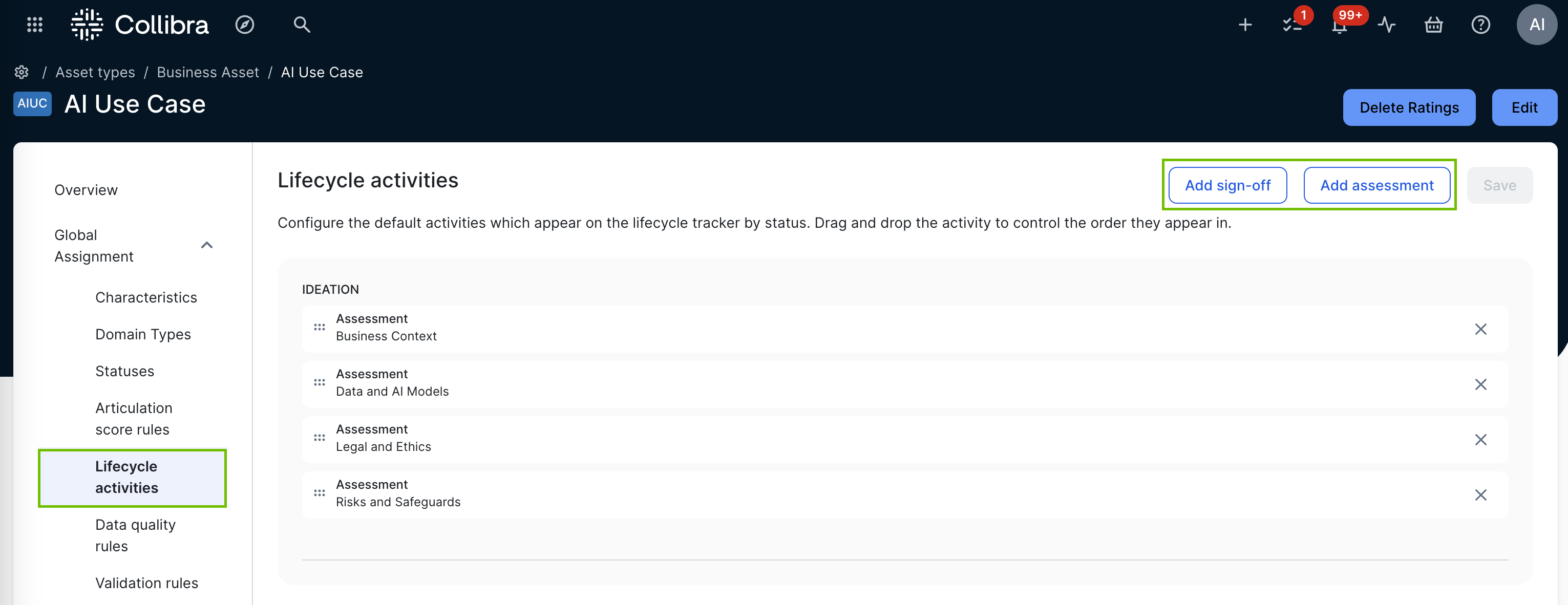
Configuring lifecycle activities in the global assignment
Also on the Lifecycle tab of an asset type's assignment, you can specify the assessment types and sign-off activities that are automatically added to the Lifecycle tracker at each lifecycle stage when you create an asset.
For more information, including required permissions, go to:
Manually adding lifecycle activities to the Lifecycle tracker
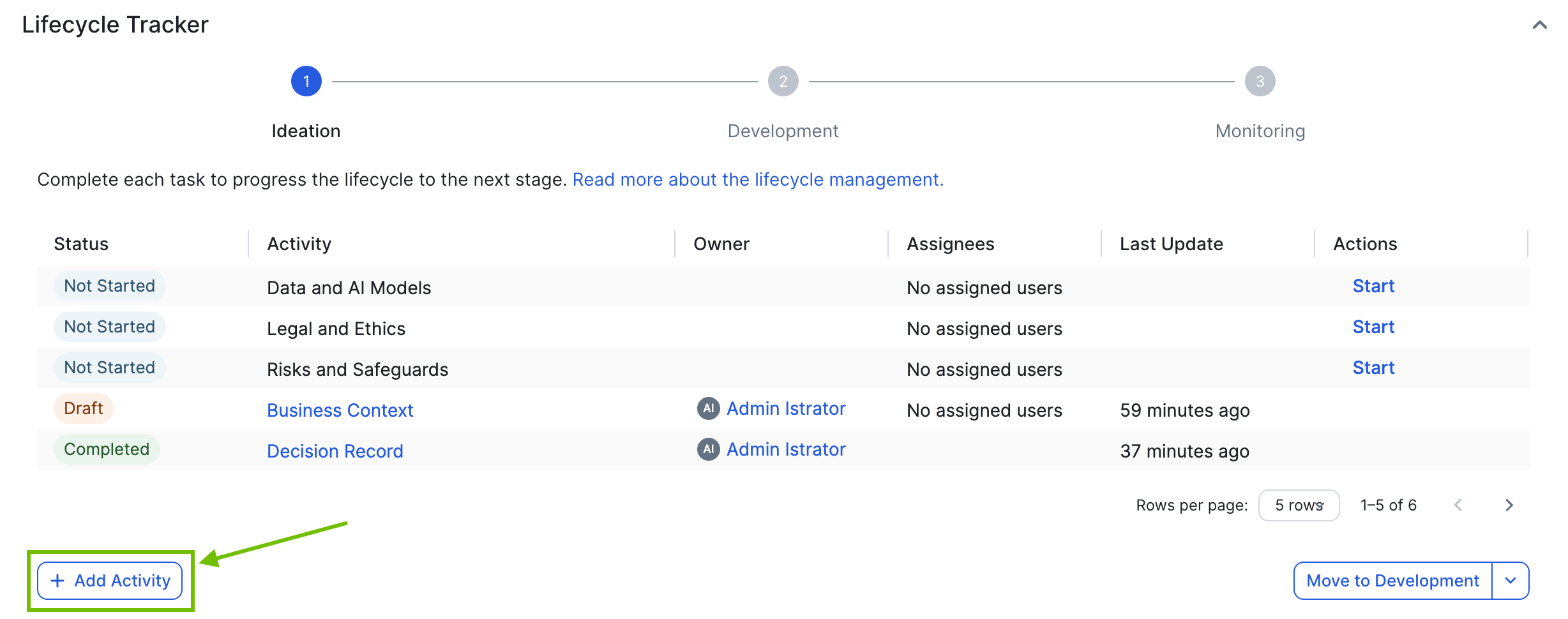
In addition to configuring lifecycle activities in the global assignment, you can also manually add assessment types and sign-off activities to the Lifecycle tracker.
Important The manual addition of assessments to the Lifecycle tracker is temporarily unavailable. This feature will be restored in the next Collibra release. You can still configure assessments for an asset type and conduct an assessment of an asset.
For more information, including required permissions, go to Add lifecycle activities to the Lifecycle tracker.
Advancing an asset through the lifecycle
After all required activities in the Lifecycle tracker have been completed, you can click Move to <stage>, to advance to the next lifecycle stage.
Note The button is shown only to users that have a resource role with the Asset > Update Status resource permission on the community or domain in which the asset is stored.
Tip In the Lifecycle tracker, required activities have the value "Required" in the Priority column.
The lifecycle stages that are configured in the asset status core phase are reflected in the Move to <stage> button and the drop-down list.
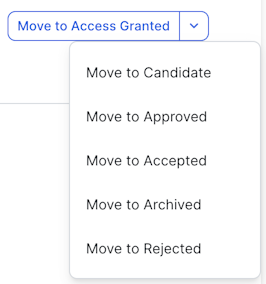
If necessary, you can use the Move to <stage> button to revert to a previous lifecycle stage. The status of the asset is updated to match. Any incomplete assessments that are not identified as "Required" are not carried over to the next stage.