When you open AI Governance, you arrive at the landing page. In the submenu, there are three submenu pages, each serving a specific purpose.

- AI Governance landing page
- AI Legal Reviews
- AI Use Cases
- AI Models
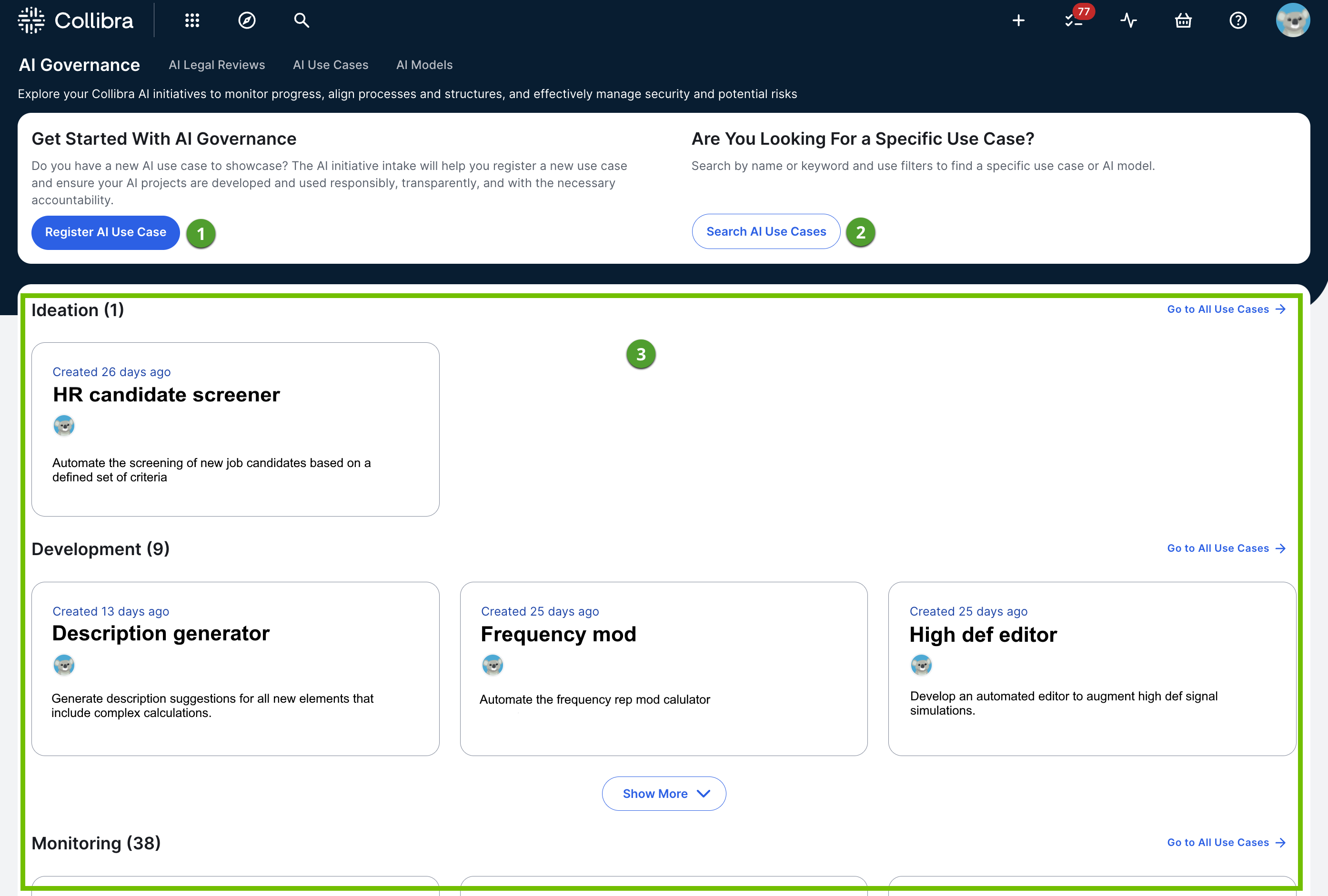
The AI Governance landing page allows you to view up to 50 existing AI use cases and register new use cases.
| No. | Element | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Register AI Use Case button |
Opens the Register AI Use Case dialog box. Note You can also create an AI Use Case asset via the global Create button. When you create an asset that way, no assessments are started. This is helpful if you want to add details to the various sections of the asset page, without the values being overwritten by an assessment. |
|
|
Search AI Use Cases |
Opens the Search page. The asterisk (*) wildcard search is run with a filter applied for th AI Use Case asset type, meaning all existing AI Use Case assets are shown in the search results. |
|
|
Use cases |
View of all AI use cases in your Collibra environment, organized by status. The statuses by which assets are organized on this page are determined by the asset statuses that are included in the AI Use Case asset type core path. If you edit the core path, the changes are reflected on the landing page. For more information, go to Configure AI Use Case asset statuses. Assets with the status Archived don't appear on the landing page, even if the status Archived is included in the AI Use Case asset type core path. Tip For information on advancing the status, or lifecycle stage, of an AI use case, go to Progress Tracker. |
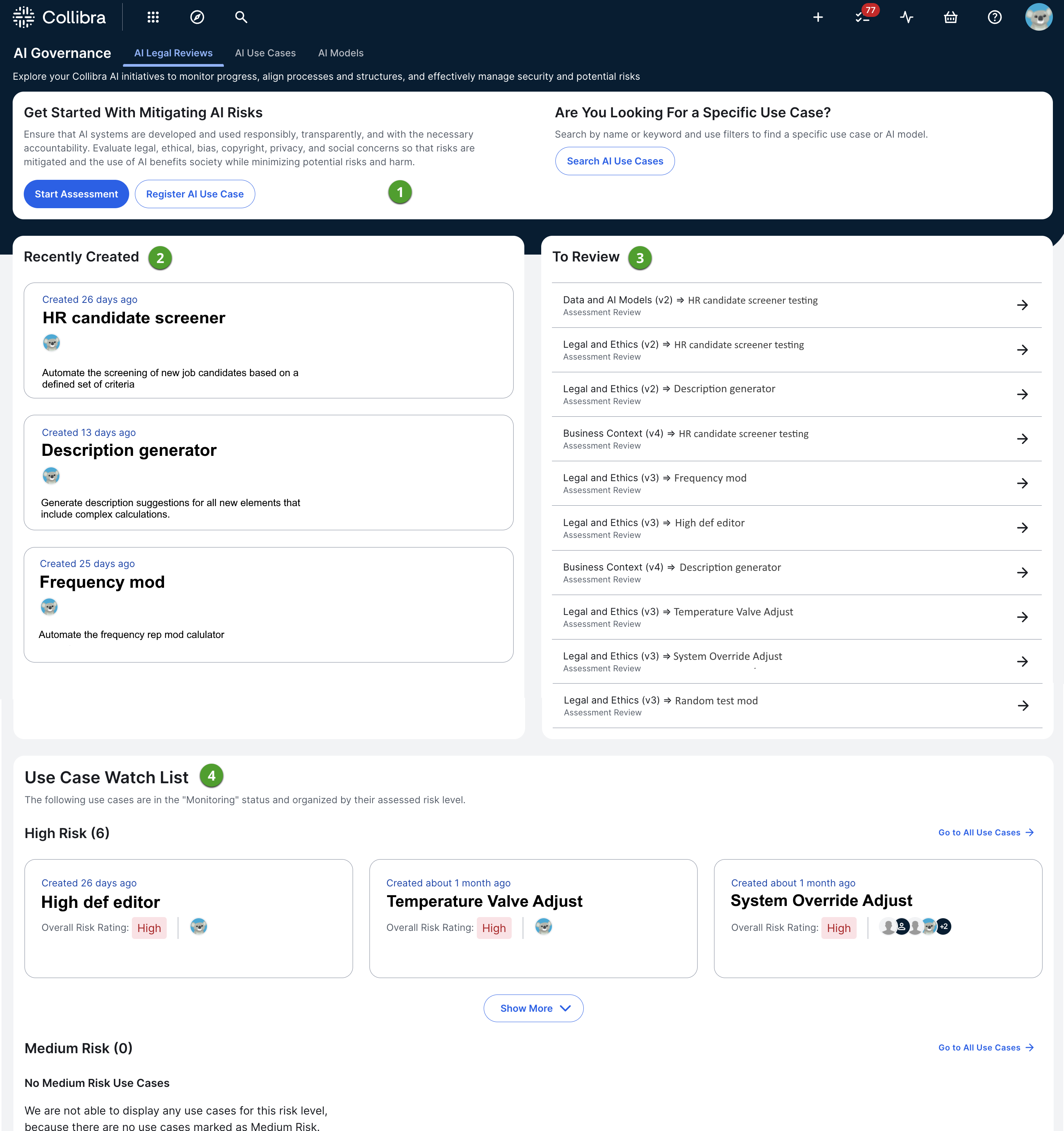
The AI Legal Reviews submenu page allows you to start assessments on new AI use cases, monitor existing and newly created use cases, register new use cases, and see which review tasks are awaiting action from you.
| No. | Element | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Start Assessment button |
Starts a Legal and Ethics assessment. For more information, go to Conduct an assessment of an AI Use Case asset. Tip You can also start any of the assessments from the Progress Tracker. |
| Register AI Use Case button | Opens the Register AI Use Case dialog box. Note You can also create an AI Use Case asset via the global Create button. When you create an asset that way, no assessments are started. This is helpful if you want to add details to the various sections of the asset page, without the values being overwritten by an assessment. |
|
|
Search AI Use Cases button |
Opens the Search page. The asterisk (*) wildcard search is run with a filter applied for th AI Use Case asset type, meaning all existing AI Use Case assets are shown in the search results. |
|
|
|
Recently Created |
Shows the three most recently registered AI use cases. |
|
|
To Review |
Shows the Assessment Review assets for which you have an approval task pending. The oldest tasks are shown, up to a maximum of 10. Click a review item to open the respective Assessment Review asset page. Note Tasks related to Assessment Review assets that have the status New, Accepted, Rejected, or Obsolete do not appear in this list. |
|
|
Use Case Watch List |
Shows existing AI use cases, grouped by risk level. This section shows only the AI use cases that are in the last stage of the AI use case lifecycle; in other words, the last asset status in the core path. For more information on the lifecycle stages of an AI use case, the core path, and configuring the asset status progression, go to: You can use the following risk rating definitions to help guide your risk assessment of your AI use cases.
Note These risk ratings are not derived or calculated. They reflect your answer – high, medium, or low – to a question in the out-of-the-box Risks and Safeguards assessment. |
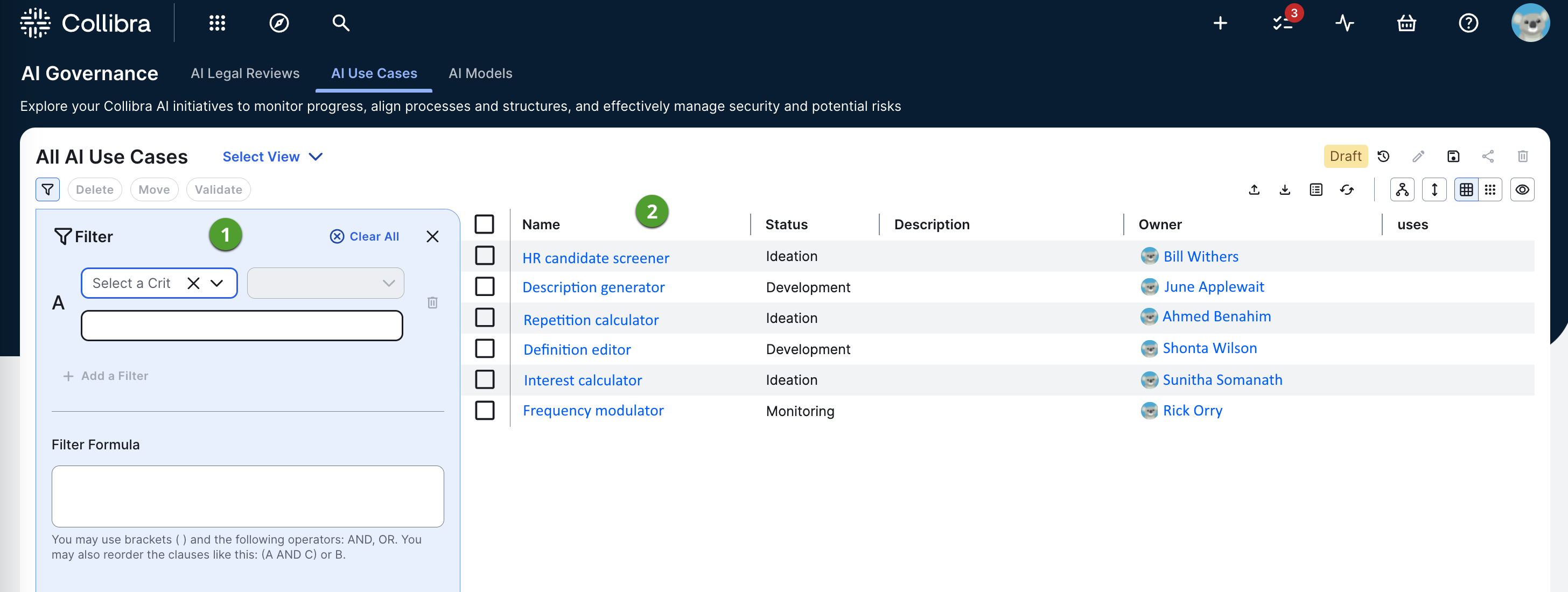
The AI use case submenu page allows you to view and search across all existing AI use cases.
| No. | Element | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
AI use case filter |
The asset filter enables you to quickly find the use cases you want by limiting the number of use cases shown in the table or set of tiles. |
|
|
Asset view |
Asset view of all existing AI use cases in your Collibra environment. |
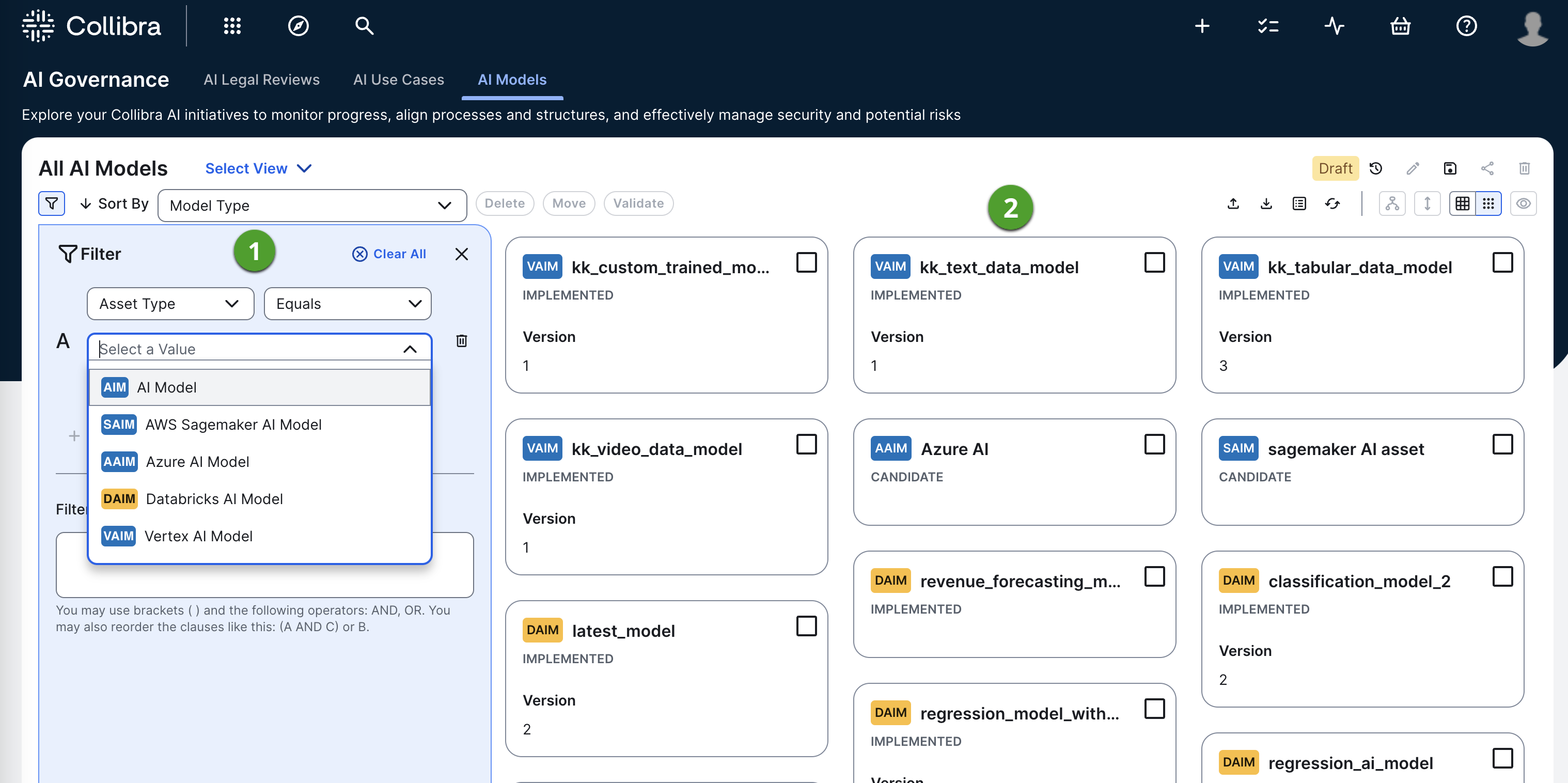
The AI model submenu page allows you to view and search across all existing AI models in your Collibra environment.
| No. | Element | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
AI model filter |
The asset filter enables you to quickly find the use cases you want by limiting the number of use cases shown in the table or set of tiles. |
|
|
Asset view |
Asset view of all existing AI models in your Collibra environment. |



