You can create data classes in multiple locations:
- The Data Classification page in the Stewardship application.
- The asset pages where you can update the classification, such as Column asset pages.
- Asset views where the Data Classification column has been added.
- If you want to use automatic data classification, create data classes on the Data Classification page in the Stewardship application. This allows immediate configuration of the classification rules.
- To add classification rules to a data class, or to update and delete data classes, you must always go to the Data Classification page in the Stewardship application.
Prerequisites
- You have a global role that has the Product Rights > Catalog global permission.
- You have a global role that has the Data Stewardship Manager global permission.
- You have a global role that has the Classification > Data Classes > Read global permission.
- You have a global role that has the Classification > Data Classes > Add global permission.
For more information, go to Required permissions.
Steps
-
On the main toolbar, click
→ Stewardship.
- Click the Data Classification tab.
- If the data class doesn't exist yet:
- Click Add.
- Type the name of the data class and press Enter.
- Click Create.
- Hover over the data class name and click Preview.
The data class parameters appear in a pane on the right-hand side. - Optionally, change the name by clicking the Name field, typing the name, and clicking the Save icon.
- Make sure the data class is enabled, unless you don't want the data classification process to use it yet.
- Optionally, add a description by clicking the Description field, typing the description, and clicking the Save icon.
- Open the Details section.
- Complete the fields as required.
Data class element Description Minimum confidence thresholdThe confidence percentage that must be reached for the data class to be considered as a possible classification result. The confidence percentage refers to the percentage of values in a column that match at least one of the classification rules in a data class, for example, the regular expression.
Enter a value between 0 and 100.
The default value is 0.Example If you add value 80 in this field, this data class will be suggested by the automatic data classification process only if the confidence percentage reaches 80 percent or higher.
Tip Confidence scores of 0 are never taken into account.
Include empty valuesInclude empty values indicates if you want to include empty values in the confidence percentage calculation.
The possible values are:- Yes: If the value is set to true, empty values are taken into account by the data classification process when calculating the confidence percentage of a matching data class.
- No (default): If the value is set to false, only the non-empty values are taken into account by the data classification process when calculating the confidence percentage of a matching data class.
This option can be used to receive an accurate confidence score for all data in a column.
ExampleYou have a column Z with 40 empty values and 60 phone numbers. You have a data class A with a regular expression to detect US phone numbers.
- If you set this option to False and you classify column Z, data class A could be suggested with a confidence percentage of 100.
- If you set this option to True and you classify column Z , data class A could be suggested but with a confidence percentage of only 60.
Important Some regular expressions are constructed to allow a match with empty values. This means that, through the regular expression, empty values can be matched to the data class, which affects the confidence score.
Example:
This expression won't match empty values with the email data class:^([a-zA-Z0-9._%\-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.\-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,6})$
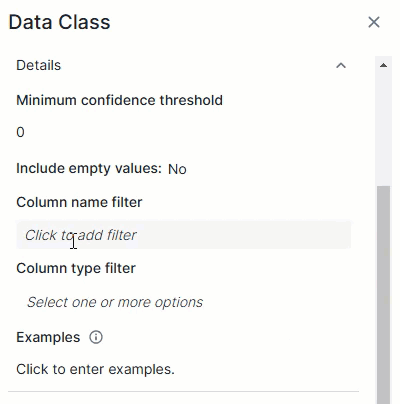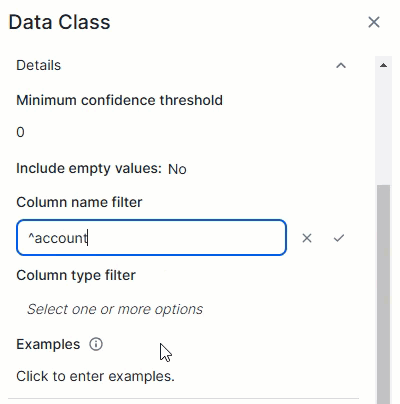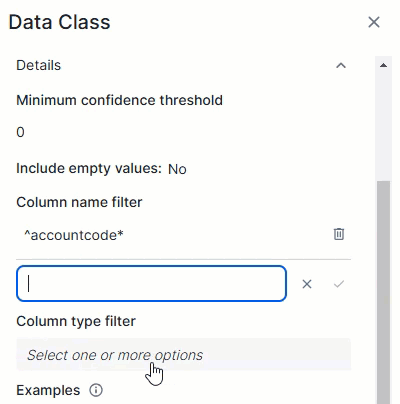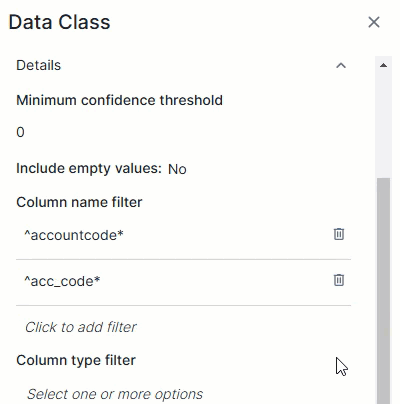
This expression will match empty values with the email data class:^([a-zA-Z0-9._%\-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.\-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,6})*$Column name filterThe Column name filter allows you to limit a data class to specific columns based on their name in the data source. The data class is considered only if the column's name in the data source matches one of the regular expressions in the filter.Add each regular expression in a separate field. To do so, enter one regular expression and click Save. A new filter field becomes available.
TipYou can add up to 25 regular expressions in the Column name filter.
Column type filterThe Column type filter allows you to limit a data class to specific column types based on their data type in the data source. The data class will be considered only if the column's data type in the data source matches one of the specified data types.Example If you select
datein the Column type filter and you classify a column with data type BIGINT in the data source, the column won't be checked against this data class.Tip Using the column type filter makes the classification of dates, times, and time stamps easier because the data class can be restricted to those data types.
The following table shows the available options in the Column type filter and their matching SQL data types.
Option Mapped SQL data types (java.sql.Types) boolean BIT, BOOL, BOOLEAN, date DATE, DATETIME, TIME, YEAR, smalldatettime, datetimeoffset double FLOAT, DOUBLE, DOUBLE PRECISION, DECIMAL, DEC, numeric, money, smallmoney, real int TINYINT, SMALLINT, MEDIUMINT, INT, INTEGER, BIGINT string CHAR, VARCHAR, TINYTEXT, TEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, LONGTEXT, ENUM, SET,nchar, nvarchar, ntext, xml, character, cidr, inet, json, macaddr, uuid, clob timestamp TIMESTAMP ExamplesSome examples of values that match the classification rule for the data class.
Add one example per line.
To save the value, click the Save icon.
- Open the Classification rules section.
- Click Add new rule.
A data class without a classification rule can be used only for manual classification.
To allow the automatic data classification process to pick up the data class, you need to add at least one classification rule.
A data class can include multiple rules, and the rules can be of different types. - From the Type list, select the type of classification rule that you want to add to the data class. The possible values are: Regular expression for column names, Data type, Regular expression for data, and List of values for data.Tip
- Add a Regular expression for column names rule to check the name of a column in the data source.
Unlike the Column name filter, which makes the name a prerequisite to consider the data class, a rule based on name serves as a criteria to apply the data class. - Add a Data type rule to check the data type of a column in the data source.
Unlike the Column type filter, which makes the data type mandatory to consider the data class, a rule based on data type serves as a criteria to apply the data class. For an example, go to Example: Importing data classes, and starting the automatic classification for a table. - Add a Regular expression for data rule to validate a pattern, such as the format of email addresses.
- Add a List of values for data rule to check for specific, predefined options, such as T-shirt sizes.
Depending on your selection, extra fields appear.
- Add a Regular expression for column names rule to check the name of a column in the data source.
- Complete the fields as required.
Fields for Regular expression for column names:
Data class element Description Regular expressionA regular expression, also referred to as regex or regexp, is a sequence of characters that specifies a match pattern in text. Multiple regular expression grammar variants exist. We use the Java variant.
In this case, the regular expression refers to the possible column names.
Example A regular expression for the column name of email address
^*email*,^maddress.Tip- Multiple websites provide guidelines and examples of regular expressions, for example, Regexlib and RegexBuddy, or even ChatGPT.
- You can also test your regular expression on various websites, for example, Regex101 (Select the Java 8 option in the Flavor panel).
The referenced websites serve only as examples. The use of ChatGPT or other generative AI products and services is at your own risk. Collibra is not responsible for the privacy, confidentiality, or protection of the data you submit to such products or services, and has no liability for such use.
ImportantThe required format of the regular expression is different between the UI and the API. In the API backslashes must be added twice (escaped). In the UI, this is not needed.
DescriptionA description of the classification rule.
Fields for Regular expression for data:
Data class element Description Regular expressionA regular expression, also referred to as regex or regexp, is a sequence of characters that specifies a match pattern in text. Multiple regular expression grammar variants exist. We use the Java variant.
In this case, the regular expression refers to the values in the columns.
Example A regular expression for an email address can be
^[a-zA-Z0-9._%\-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.\-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,6}$Tip- Multiple websites provide guidelines and examples of regular expressions, for example, Regexlib and RegexBuddy, or even ChatGPT.
- You can also test your regular expression on various websites, for example, Regex101 (Select the Java 8 option in the Flavor panel).
The referenced websites serve only as examples. The use of ChatGPT or other generative AI products and services is at your own risk. Collibra is not responsible for the privacy, confidentiality, or protection of the data you submit to such products or services, and has no liability for such use.
ImportantThe required format of the regular expression is different between the UI and the API. In the API backslashes must be added twice (escaped). In the UI, this is not needed. For example: In the
UI, use^\+?\d{1,3}?\d{1,4}$, and in the API, use^\\+?\d{1,3}?\\d{1,4}$.DescriptionA description of the classification rule.
Fields for List of values for data:
Data class element Description Upload a fileUse this to upload a csv file with possible data class values. The file must contain one value per line. The maximum file size of 100 MB.
This method is mandatory if you want to add more than 1,000 values.
Download fileIf you download a file, the name of the file is: listofvalues_ID of the data class rule.
ValuesAdd the values that define a specific data class.
ExampleA data class for T-shirt sizes based on a list of values could be:
SMLsmallmediumlargeImportant- Add only one value per line.
- The maximum number of characters in a single list value is 10,000.
- Don’t add any leading or trailing blank characters in a value.
- The values are not case-sensitive, the value “small” in the list will also be a match with the values “Small” and “SMALL”.
- The maximum total number of values in one data class is 25,000. This number can be spread over multiple classification rules.
DescriptionA description of the classification rule.
Field for Data type:
Data class element Description Data TypeSelect one or more data types.During the automatic data classification, the data type of the column in the data source is verified against the selected data types in this classification rule.
Tip Using this type of rule makes the classification of dates, times, and time stamps easier because you can check based on data type.
Example You create a rule with data type
dateand you classify a column with a data type DATETIME in the data source. As a result, the column will be classified with this data class.The following table shows the available options in the Data Type field and their matching SQL data types.
Option Mapped SQL data types (java.sql.Types) boolean BIT, BOOL, BOOLEAN, date DATE, DATETIME, TIME, YEAR, smalldatettime, datetimeoffset double FLOAT, DOUBLE, DOUBLE PRECISION, DECIMAL, DEC, numeric, money, smallmoney, real int TINYINT, SMALLINT, MEDIUMINT, INT, INTEGER, BIGINT string CHAR, VARCHAR, TINYTEXT, TEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, LONGTEXT, ENUM, SET,nchar, nvarchar, ntext, xml, character, cidr, inet, json, macaddr, uuid, clob timestamp TIMESTAMP DescriptionA description of the classification rule.
- Multiple websites provide guidelines and examples of regular expressions, for example, Regexlib and RegexBuddy, or even ChatGPT.
- Click Save.
The classification rule for the data class is configured.
A new section appears. If you expand the section, the details are shown. - If needed, click Add new rule to add another classification rule to the data class.
- You can combine regular expression for column names, regular expression for data, list of values for data, and data type rules in one data class.
- The maximum number of rules in a data class is 25.
- During the automatic data classification process, each rule is verified and the data class is assigned as soon as one of the rules applies.
ImportantBy default, rules based on column name and data type are evaluated before rules based on samples, such as regular expressions for data and lists of values for data. Rules based on samples are evaluated in the order in which they appear in the data class.
Show more informationIf the name of the Column asset matches the regular expression in the classification rule, the data class is applied, and no other rules are checked for that column.
If the column's data type in the data source matches the data type in the classification rule, the data class is applied, and no other rules are checked for that column.
If the column name and data type don't match, sample data from the column is evaluated against the other rules in the data class. These rules are processed in the order of appearance in the data class. When a rule matches a sample, the sample is considered a match, and the confidence score of the data class increases. At this point, the remaining rules are skipped for that sample. In that sense, it's important to add rules that are more likely to produce a match before others.
Go to some examples
Import out-of-the-box data classes
Merge data classes
Helpful resources
Contextualize your data with Unified Data Classification course in Collibra University