In Collibra 2024.05, we launched a new user interface (UI) for Collibra Platform! You can learn more about this latest UI in the UI overview.
Use the following options to see the documentation in the latest UI or in the previous, classic UI:
A complex relation is a characteristic that describes how two or more assets relate to each other. It can also have attributes of its own, for example, Description and Priority. Technically, they are objectified associations: simplified assets that cannot exist independently. The type of a complex relation defines the relations and attributes the complex relation can have.
You can add a complex relation between assets if the complex relation's type is in the relevant assignment of the asset's type.
Note A complex relation cannot have more than 32,767 relations to assets.
Example
When you add a complex relation, you add one or more relations between the assets and the complex relation itself. The assets of those relations are always the head of the relation, while the complex relation is always the tail.
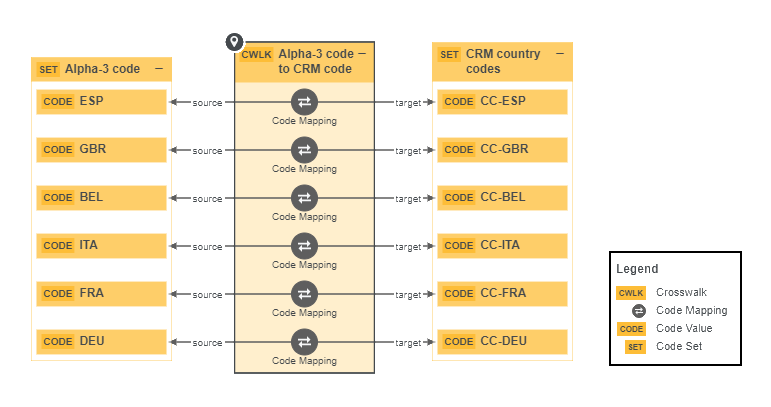
The following example creates a complex relation type called Code Mapping, with three relation types (source, target and crosswalk) and two attribute types (Description and Transformation Logic).
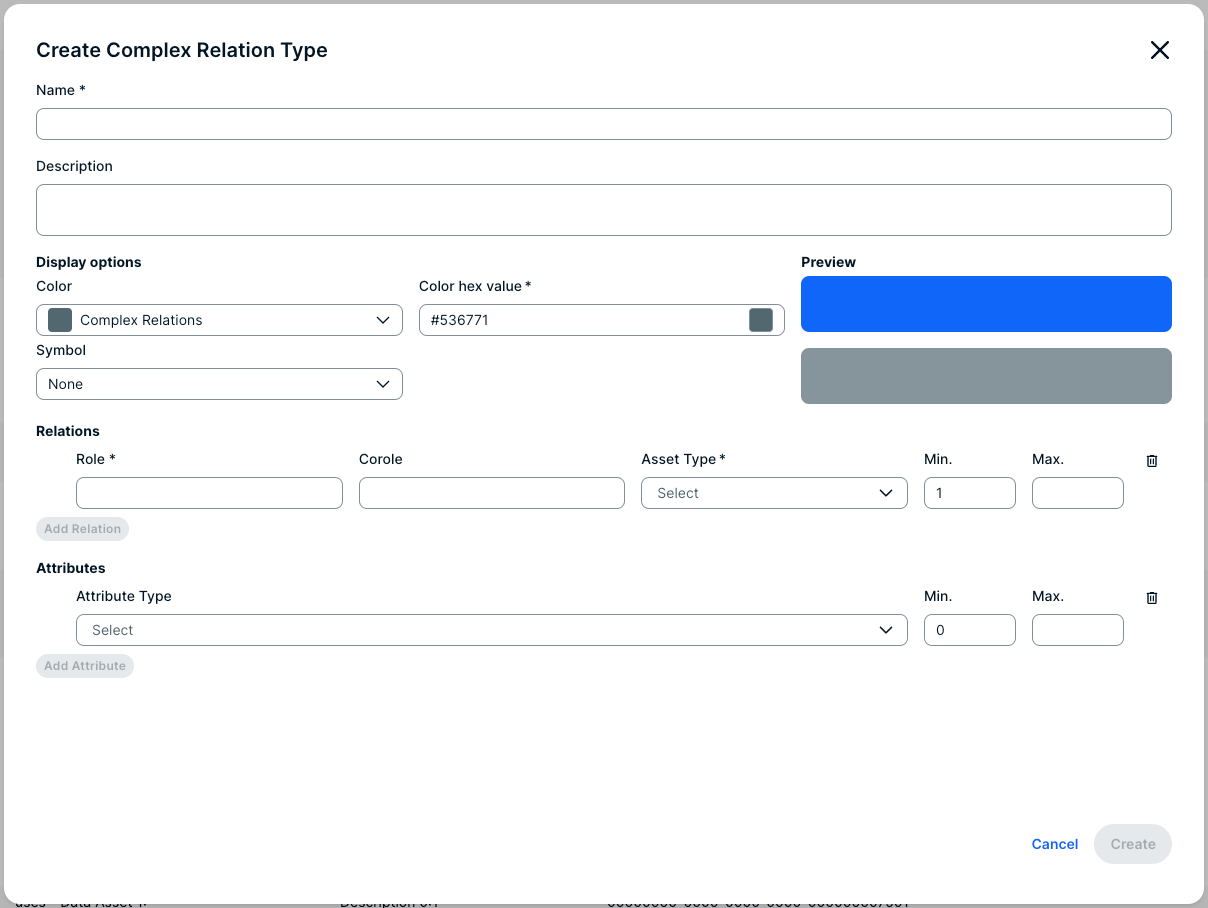
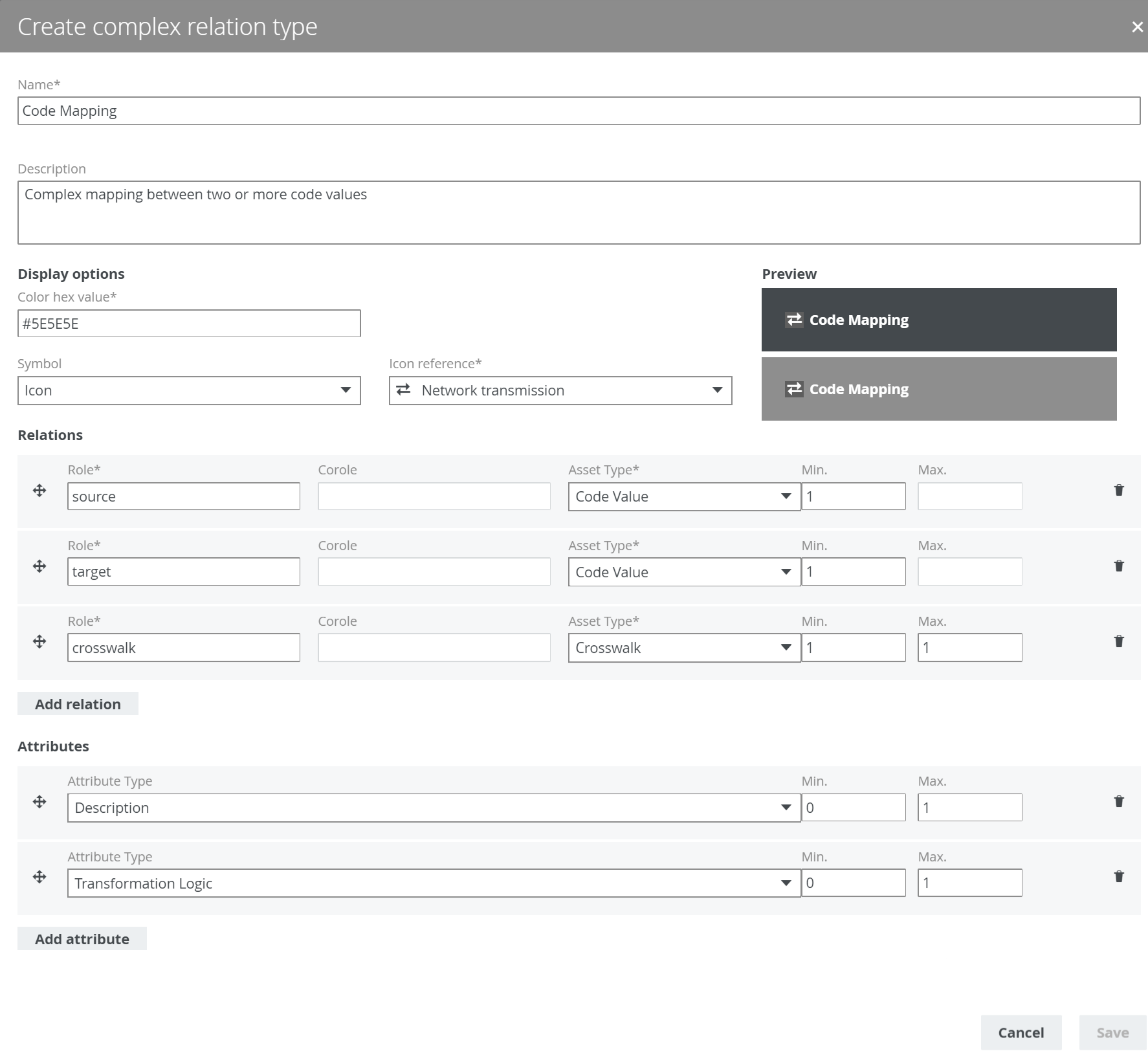
For each relation type in the complex relation type, you can select head assets. Above the fields, you can see the minimum and maximum occurrences for each relation type. For each selected head asset, a relation of the relevant type is created between the head asset and the complex relation. You can also add attributes to the complex relation.
Cardinality of relation types and attribute types in complex relation types
With complex relations, you can associate two or more assets in a relation and add attributes to the complex relation. When you create a complex relation type, you set the cardinality of the relation types and attribute types to determine how many relations and attributes you can or must provide when you create a complex relation of that type.
Tip For every complex relation type, at least one relation type must have a minimum cardinality of 1 or greater.