In Collibra Platform, you can:
- Register individual Google BigQuery databases via the BigQuery JDBC driver.
- Integrate a Google Cloud Storage (GCS) file system.
- Integrate metadata from projects in Google Dataplex.
- Integrate Entries and Aspects from Google Dataplex Universal Catalog.
It is important to understand the different ways of working with GCP because the resulting data in Collibra varies.
| Possible ways to work with GCP | Result in Collibra |
|---|---|
| Integrating Google Dataplex - Dataplex Universal Catalog integration |
Google Dataplex Universal Catalog is a technical catalog from Google that provides information for all the data in various Dataplex projects. The Dataplex Universal Catalog integration creates assets that represent Views, Entries, and Aspects from Dataplex Universal Catalog in Collibra Platform. With the Dataplex Universal Catalog integration, you can retrieve sample data and also profile and classify the data. This feature is in preview. To learn how to integrate Dataplex Universal Catalog with sampling, profiling, and classification, go to Steps: Integrate Google Dataplex Universal Catalog via Edge. When you integrate Dataplex Universal Catalog, BigQuery metadata is also integrated. For more information about integrating BigQuery through a Dataplex Universal Catalog integration or the BigQuery JDBC connector, go to Ways to integrate Google BigQuery data sources. |
| Integrating Google Dataplex - Dataplex ingestion |
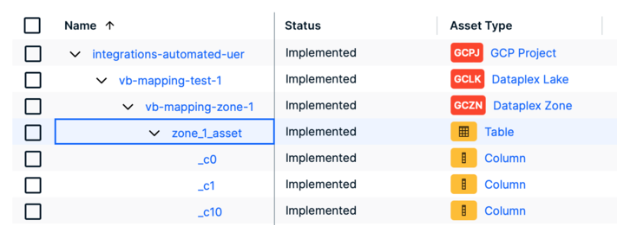
Google Dataplex is a technical catalog from Google that provides information for all the data in various Dataplex projects. The Google Dataplex ingestion registers and synchronizes GCP Projects, Dataplex Lakes, Dataplex Zones, Tables, and Columns. The integration creates the whole asset structure, representing Dataplex objects such as Project, Lake, Zone, Table, and Column, and allows you to filter based on Lakes and Zones. Note Google Dataplex ingestion is no longer in active development and will only update for defect fixes. Consider using the Dataplex Universal Catalog ingestion via Edge instead.
|
|
The Google Cloud Storage (GCS) file system integration allows you to register Google Cloud Storage (GCS) as a data source in Collibra and synchronize metadata. The GCS integration supports Google Dataplex, a service used for schema discovery. This allows you to integrate schemas, tables, and columns from the files and create a File Group asset in Collibra rather than multiple File assets. The GCS integration integrates data from GCS based on the configured crawler. It also adds Tables and Columns recognized by Dataplex, which are related to files and file groups. |
|
| Register a Google BigQuery database |
If you register a specific Google BigQuery data source via the BigQuery JDBC connector, the resulting assets represent the tables and columns in the database. You can retrieve sample data and also profile and classify the data. For more information about integrating BigQuery through a Dataplex Universal Catalog integration or the JDBC connector, go to Ways to integrate Google BigQuery data sources. |
Helpful resources
To learn more about working with Google Cloud Platform, follow our University course.