Create a custom technical lineage
You can create a custom technical lineage to include metadata of data sources that are not supported.
You can create two types of custom technical lineages:
- A simple custom technical lineage, which defines a basic object hierarchy and creates a lineage between two or more data objects.
- An advanced custom technical lineage, which contains a simple predefined technical lineage and defines transformations to create the lineage.
Note In the local folder that you need to create, you can only have one JSON file. You can, however, add other files in the harvested directory and subdirectories and refer to those files from within the JSON file.
Prerequisites
- You have downloaded the lineage harvester and you have the necessary system requirements to run it.
- You have the necessary permissions for all database objects that the lineage harvester accesses.
- You have prepared the physical data layer in Data Catalog.
Create a simple custom technical lineages
- Create a local folder.
- Create a new JSON file in the local folder.
- Name the JSON file lineage.json.
- Add the following mandatory sections to the JSON file:
Properties
Description version
The version of the JSON architecture.
Note Currently, you can only use version 1.0.
This section contains tree definitions of data objects between which lineages can be defined. Each node of a tree contains the name, type and optionally children or leaves properties which form a hierarchy of data objects. You can reuse the same properties in one node to map all data objects in the hierarchy.
Tip Usually, the structure you map is the following: system > database > schema > table > column. The system is optional, unless the
useCollibraSystemNameproperty is set totruein the lineage harvester configuration file. The Collibra Data Lineage can stitch these data objects to assets in Data Catalog. However, you can also map custom objects, for example dashboards and reports. Custom objects cannot be stitched to assets in Data Catalog.nameThe name of your data object. This is the system name, database name, schema name, table name or column name.
Warning
- The names are case sensitive.
- The names of data objects of the same type must be unique.
typeThe type of your data object. For example:
system,database,schema,tableorcolumn.childrenThe sub-objects that have a hierarchical relation to the defined data object. Each child also has the
nameandtypeproperties and can have children of its own, except for the penultimate child which has leaves instead of children. Leaves are children without children.Note Use the children property to define sub-objects, but use the leaves property if the object is on the penultimate level. For example, to define columns that have a relation to a table node.
leavesThe sub-objects of another sub-object that is defined in a
childrenproperty, but cannot have sub-objects of their own.Note Technical lineage only shows relations between leaf nodes of the tree. Leaves are usually columns that have a relation to a table node in the tree structure.
lineages This section contains the path from a source to a target and defines the mappings and transformations that should be processed by the Collibra Data Lineage server.
Note If you create a lineage between data objects that are also assets in Data Catalog, the Collibra Data Lineage server automatically stitches the data objects to the assets in Data Catalog. However, you can also create a lineage between custom data objects that are not assets in Data Catalog, for example reports and dashboards.
src_pathThe hierarchical path to the source data object. This data object is shown as a leaf in the tree node.
<data objects>All data object names in the hierarchical path to the source leaf.
Example of data objects that can be stitched: system > database > schema > table > column.
Example of data objects that cannot be stitched: dashboard > report > column.
trg_pathThe hierarchical path to the target data object. This data object is shown as a leaf in the tree node.
<data objects>All data object names in the hierarchical path to the target leaf.
Example of data objects that can be stitched: system > database > schema > table > column.
Example of data objects that cannot be stitched: dashboard > report > column.
mappingThe mapping name. This refers to the queries used in the technical lineage.
source_codeThe transformation code. This determines how the technical lineage is constructed.
Tip The source code can be a SQL statement or code that manipulates data.
See an example whenuseCollibraSystemNameis set tofalse.This is an example of a JSON file for a simple custom lineage. The
useCollibraSystemNamein the lineage harvester configuration file is set tofalse. As a result, system data objects are optional.Tip Click
 to copy the example to your clipboard.
to copy the example to your clipboard.
{ "version": "1.0", "tree": [ { "name": "UserDB", "type": "database", "children": [ { "name": "SCH", "type": "schema", "children": [ { "name": "users", "type": "table", "leaves": [ { "name": "membership_type", "type": "column" } ] } ] } ] }, { "name": "User dash", "type": "dashboard", "children": [ { "name": "Memberships", "type": "report", "leaves": [ { "name": "Type", "type": "column" } ] } ] } ], "lineages": [ { "src_path": [ {"database": "UserDB"}, {"schema": "SCH"}, {"table": "users"}, {"column": "membership_type"} ], "trg_path": [ {"dashboard": "User dash"}, {"report": "Memberships"}, {"column": "Type"} ], "mapping": "make_report", "source_code": "report = rep(data)" } ] }This image shows the result of the custom lineage in Data Catalog.
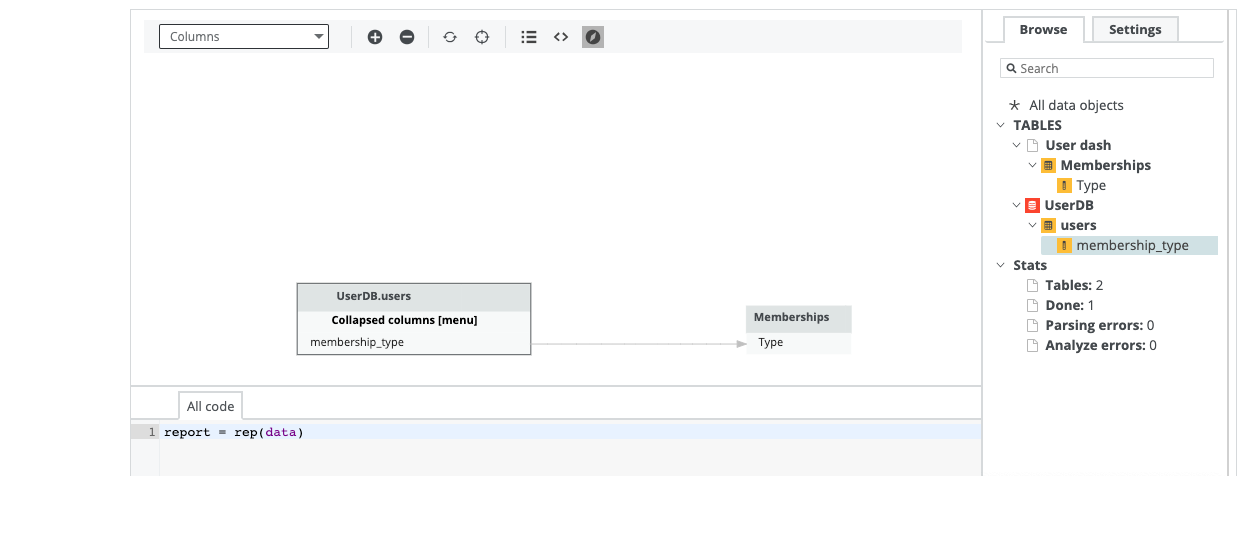 See an example when
See an example whenuseCollibraSystemNameis set totrue.This is an example of a JSON file for a simple custom lineage. The
useCollibraSystemNamein the lineage harvester configuration file is set totrue. As a result, you have to include system data objects.Tip Click
 to copy the example to your clipboard.
to copy the example to your clipboard.
{ "version": "1.0", "tree": [ { "name": "CollibraSystem1", "type": "system", "children": [ { "name": "DB1", "type": "database", "children": [ { "name": "DEFAULT", "type": "schema", "children": [ { "name": "TB1", "type": "table", "leaves": [ { "name": "COL1", "type": "column" } ] } ] } ] } ] }, { "name": "CollibraSystem2", "type": "system", "children": [ { "name": "DB2", "type": "database", "children": [ { "name": "DEFAULT2", "type": "schema", "children": [ { "name": "TB2", "type": "table", "leaves": [ { "name": "COL2", "type": "column" } ] } ] } ] } ] } ], "lineages": [ { "src_path": [ {"system": "CollibraSystem1"}, {"database": "DB1"}, {"schema": "DEFAULT"}, {"table": "TB1"}, {"column": "COL1"} ], "trg_path": [ {"system": "CollibraSystem2"}, {"database": "DB2"}, {"schema": "DEFAULT2"}, {"table": "TB2"}, {"column": "COL2"} ], "mapping": "CMAPPER", "source_code": "C1 > C2" } ] } - In your configuration file, add the path to the JSON file.
Create an advanced custom technical lineage
- Create a local folder.
- Create a new JSON file in the local folder.
- Name the JSON file lineage.json.
- In the same local folder, store all of the source codes that you want to reference in the JSON file.
- Add the following sections to the JSON file:
Properties
Description version
The version of the JSON architecture.
Note Currently, you can only use version 1.0.
This section contains tree definitions of data objects between which lineages can be defined. Each node of a tree contains the name, type and optionally children or leaves properties which form a hierarchy of data objects. You can reuse the same properties in one node to map all data objects in the hierarchy.
Tip Usually, the structure you map is the following: system > database > schema > table > column. The system is optional, unless the
useCollibraSystemNameproperty is set totruein the lineage harvester configuration file. The Collibra Data Lineage can stitch these data objects to assets in Data Catalog. However, you can also map custom objects, for example dashboards and reports. Custom objects cannot be stitched to assets in Data Catalog.nameThe name of your data object. This is the system name, database name, schema name, table name or column name.
Warning
- The names are case sensitive.
- The names of data objects of the same type must be unique.
typeThe type of your data object. For example:
system,database,schema,tableorcolumn.childrenThe sub-objects that have a hierarchical relation to the defined data object. Each child also has the
nameandtypeproperties and can have children of its own, except for the penultimate child which has leaves instead of children. Leaves are children without children.Note Use the children property to define sub-objects, but use the leaves property if the object is on the penultimate level. For example, to define columns that have a relation to a table node.
leavesThe sub-objects of another sub-object that is defined in a
childrenproperty, but cannot have sub-objects of their own.Note Technical lineage only shows relations between leaf nodes of the tree. Leaves are usually columns that have a relation to a table node in the tree structure.
lineages This section contains the path from a source to a target and defines the mappings and transformations that should be processed by the Collibra Data Lineage server.
Note If you create a lineage between data objects that are also assets in Data Catalog, the Collibra Data Lineage server automatically stitches the data objects to the assets in Data Catalog. However, you can also create a lineage between custom data objects that are not assets in Data Catalog, for example reports and dashboards.
src_pathThe hierarchical path to the source data object. This data object is shown as a leaf in the tree node.
<data objects>All data object names in the hierarchical path to the source leaf.
Example of data objects that can be stitched: system > database > schema > table > column.
Example of data objects that cannot be stitched: dashboard > report > column.
trg_pathThe hierarchical path to the target data object. This data object is shown as a leaf in the tree node.
<data objects>All data object names in the hierarchical path to the target leaf.
Example of data objects that can be stitched: system > database > schema > table > column.
Example of data objects that cannot be stitched: dashboard > report > column.
mapping_refThe mapping of the source codes that are located in the same directory of the JSON file and their positions in the technical lineage.
Note The positions are zero based. The first character in a sequence has position 0.
source_codeThe source code for which you provide a path in the
codebase_filesnode.Tip The source code can be a SQL statement or code that manipulates data.
mappingThe mapping name of the mapping defined in the
codebase_filesnode.codebase_posThe positions of a source code file that is located in the same directory of the JSON file. These source code positions will be highlighted under the technical lineage of a column.
codebase_files
This section defines the reference to source code files that are stored in the same directory as the JSON file.
<source code path>The reference to source code that is located in the same directory as the JSON file. This contains mappings of the source codes and their positions.
mapping_refsThe mapping of the source code for which you provided the path in <source code path>.
See an example whenuseCollibraSystemNameis set tofalse.This is an example of a JSON file for an advanced custom lineage. The
useCollibraSystemNamein the lineage harvester configuration file is set tofalse. As a result, system data objects are optional.The following example references
user_utils.py, which is source code that is stored in the same directory as the JSON file.Tip Click
 to copy the example to your clipboard.
to copy the example to your clipboard.
{ "version": "1.0", "tree": [ { "name": "UserDB", "type": "database", "children": [ { "name": "SCH", "type": "schema", "children": [ { "name": "users", "type": "table", "leaves": [ { "name": "membership_type", "type": "column" } ] } ] } ] }, { "name": "User dash", "type": "dashboard", "children": [ { "name": "Memberships", "type": "report", "leaves": [ { "name": "Type", "type": "column" } ] } ] } ], "lineages": [ { "src_path": [ {"database": "UserDB"}, {"schema": "SCH"}, {"table": "users"}, {"column": "membership_type"} ], "trg_path": [ {"dashboard": "User dash"}, {"report": "Memberships"}, {"column": "Type"} ], "mapping_ref": { "source_code": "user_utils.py", "mapping": "showUserData", "codebase_pos": [ { "pos_start": 25, "pos_len": 31 } ] } } ], "codebase_files": { "user_utils.py": { "mapping_refs": { "showUserData": { "pos_start": 0, "pos_len": 56 } } } } }This example shows the contents of
user_utils.py.from db_utils import * report = make_report(user_data)
This image shows the result of the custom lineage in Data Catalog.
 See an example when
See an example whenuseCollibraSystemNameis set totrue. .This is an example of a JSON file for an advanced custom lineage. The
useCollibraSystemNamein the lineage harvester configuration file is set totrue. As a result, you have to include system data objects.The following example references
user_utils.py, which is source code that is stored in the same directory as the JSON file.Tip Click
 to copy the example to your clipboard.
to copy the example to your clipboard.
{ "version": "1.0", "tree": [ { "name": "db-system", "type": "system", "children": [ { "name": "userDB", "type": "database", "children": [ { "name": "SCH", "type": "schema", "children": [ { "name": "users", "type": "table", "leaves": [ { "name": "membership_type", "type": "column" } ] } ] } ] } ] }, { "name": "oracle-system", "type": "system", "children": [ { "name": "user-db", "type": "database", "children": [ { "name": "DEFAULT", "type": "schema", "children": [ { "name": "contact-info", "type": "table", "leaves": [ { "name": "membership", "type": "column" } ] } ] } ] } ] } ], "lineages": [ { "src_path": [ {"system": "db-system"}, {"database": "UserDB"}, {"schema": "SCH"}, {"table": "users"}, {"column": "membership_type"} ], "trg_path": [ {"system": "oracle-system"}, {"database": "user-db"}, {"schema": "DEFAULT"}, {"table": "contact-info"}, {"column": "membership"} ], "mapping_ref": { "source_code": "user_utils.py", "mapping": "showUserData", "codebase_pos": [ { "pos_start": 25, "pos_len": 31 } ] } } ], "codebase_files": { "user_utils.py": { "mapping_refs": { "showUserData": { "pos_start": 0, "pos_len": 56 } } } } }This example shows the contents of
user_utils.py.from db_utils import * report = make_report(user_data)
- In your configuration file, add the path to the JSON file.
What's next
When you're done configuring the JSON file, you can prepare the lineage harvester configuration file and enter the correct properties to create a technical lineage using the JSON file.