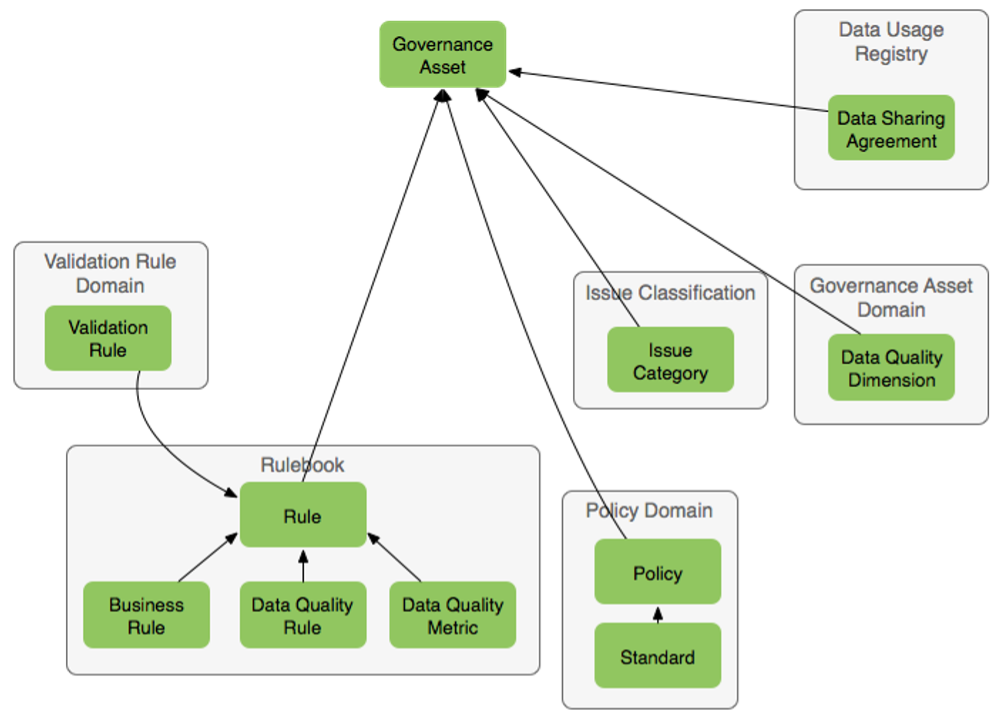
| Policy |
A statement of intent that is implemented by a set of rules. Policies are usually set by a data governance council. |
| Standard |
A specific low-level mandatory action or rule that helps to enforce and support a policy. Example: All personal information must be encrypted with a specific encryption type. |
| Regulation |
A directive made and maintained by an authority. For example, BCBS and Solvency.
|
| Purpose |
An asset that describes the reason for which another asset is created or for which another asset exists.
|
|
Legal Basis
|
The lawfulness of processing, as defined by Article 6 of GDPR. Personal data may be processed only if, and to the extent that, at least one legal basis applies. (Implicit for CCPA)
|
|
Assessment
|
A type of asset that is used to store the results of assessments as attributes and relations.
|
|
Safeguard
|
(GDPR) Safeguards for transfers of data and in particular Personal Information to third parties, other countries or international organizations.
|
| Risk |
An uncertain event that could create damage, injury, liability, loss or any other negative occurrence that is caused by external or internal vulnerabilities (Risk Sources), which can be avoided through controls. |
| Control |
A measure taken to mitigate a risk. Any process, policy, device, practice, or other conditions and/or actions which maintain and/or modify risk. |