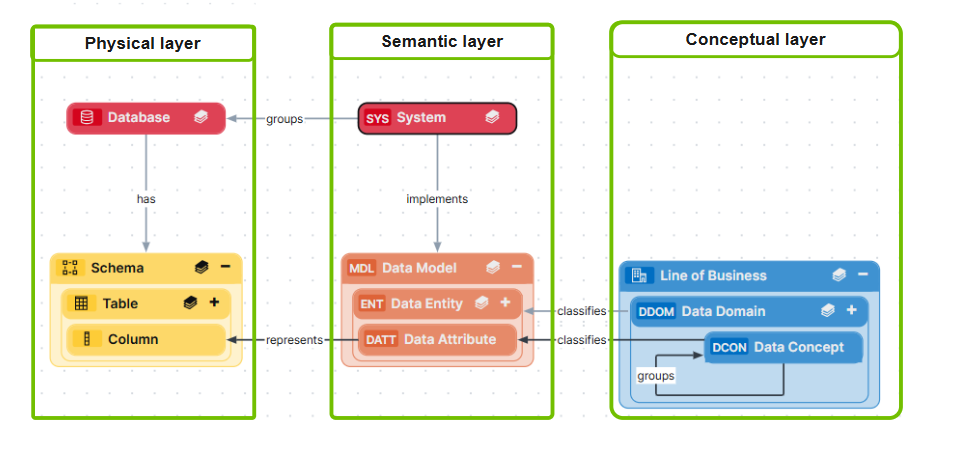
About the Guided Stewardship operating model and data layers
- The physical layer represents the actual storage-level structure of the data as they exist in the source systems. The physical layer consists of assets such as Schema, Table, and Column assets.
- The semantic layer, also referred to as the logical data layer, provides a business-centric view of data. The semantic layer consists of assets such as Data Model, Data Entity, and Data Attribute assets, which act as a bridge between the raw physical assets and the Knowledge Graph's governance assets, such as Business Term, KPI, and Data Category assets.
- The conceptual layer defines the enterprise blueprint for data, focusing on broad, system-independent Data Domains and Data Concepts. It provides a standardized way to understand data and serves as the foundation for organization-wide governance.
The Guided Stewardship operating model specifically includes the semantic layer and conceptual layer asset types, such as Data Attribute, Data Entity, Data Model, Data Concept, and Data Domain. The physical data layer asset types, Schema, Table, and Column, are available with Data Catalog.
Database and System assets are Technology assets that represent the highest level over physical data and logical data organization.
Tip The definition of all 3 layers is very useful for larger organizations that have data governance experience. For other organizations, defining the physical layer and the semantic layer can be a good starting point. If the full Guided Stewardship operating model is too complex for your organization, we advise to skip the conceptual layer because the semantic layer provides better out-of-the-box features and relation possibilities to the physical layer.
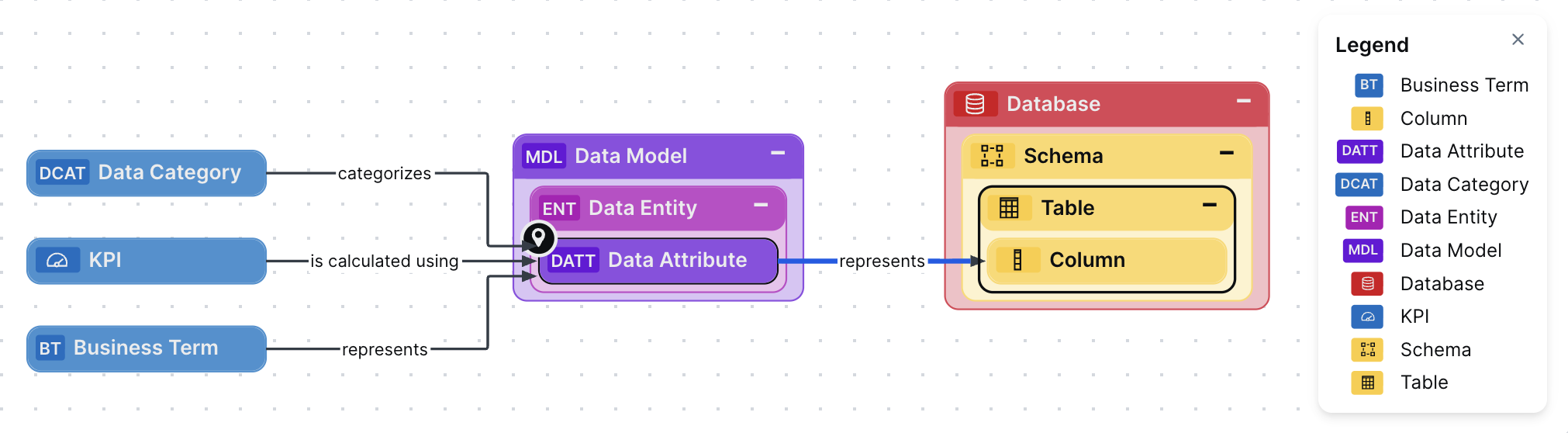
The following image shows all relevant asset types, per layer, and the relationships that bind them together in Collibra.
About the physical layer
The physical layer represents the actual data in an organization's systems. It consists of the following asset types: Database, Schema, Table, and Column.
- The Schema, Table, and Column asset types are available with Data Catalog.
The Schema, Table and Column assets are almost never created manually. They are mostly automatically created via the Data Catalog registration processes. - Although the Database asset type is a Technology asset, it is considered part of the physical layer.
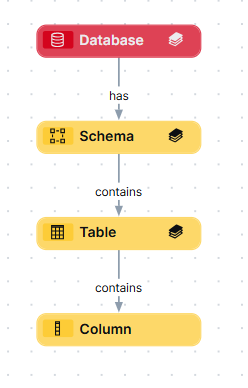
A Schema is the highest level of physical structure in a Database. It defines, in a formal language, the structure of the tables and columns in the database. Schema assets are part of the physical layer. Schema assets are related to Database assets and Table assets as follows:
|
Schema assets are related to... |
Via the relation type... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Database assets | Database has / belongs to Schema |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
| Table assets | Schema contains / is part of Table |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
Table assets represent the physical tables in a data environment. Table assets are part of the physical layer. Table assets are related to the Schema assets and Column assets as follows:
|
Table assets are related to... |
Via the relation type... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Schema assets | Table is part of / contains Schema |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
| Column assets | Table contains / is part of Column |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
Column assets represent the physical columns in a data environment. It is the lowest level of definition in the physical layer. Column assets are related to Table and Data Attribute assets as follows:
|
Column assets are related to... |
Via the relation type... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Table assets | Column is part of / contains Table |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
| Data Attribute assets | Data Attribute represents / represented by Column |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
About the semantic layer
A semantic layer makes it easier for business users to understand the meaning and context of data. The main building blocks of the semantic layer, Data Entity and Data Attributes assets, act as a bridge between physical data assets, such as databases or files, and governance assets in the Collibra Knowledge Graph, including business terms, KPIs, and data categories.
- The Data Entity and Data Attribute asset types are available with Guided Stewardship.
- Although the System asset type is a Technology asset, it is considered part of the semantic layer. Including a System asset is not mandatory in the Guided Stewardship operating model.
The semantic layer is a tree-like structure, starting with high-level System and Data Model assets, and branching out with implementation-specific Data Entity and Data Attribute assets.
{
"nodes": [
{
"id": "Column",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000031008"
},
"editorSettings": {
"nodePropsExpanded": false
},
"layoutRegion": "flow"
},
{
"id": "Data Attribute",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000031005"
}
},
{
"id": "Table",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000031007"
},
"display": "collapsed",
"layoutRegion": "context"
},
{
"id": "Schema",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0001-000400000002"
},
"layoutRegion": "context"
},
{
"id": "Data Entity",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000031004"
},
"display": "collapsed",
"layoutRegion": "context"
},
{
"id": "Data Model",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000031003"
},
"layoutRegion": "context"
},
{
"layoutRegion": "context",
"id": "Database",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000031006"
}
},
{
"id": "Data Category",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000031109"
}
},
{
"id": "KPI",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000011002"
}
},
{
"id": "Business Term",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000011001"
}
}
],
"edges": [
{
"from": "Data Attribute",
"to": "Column",
"label": "",
"style": "arrow",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000007094"
},
"roleDirection": true
},
{
"from": "Column",
"to": "Table",
"label": "",
"style": "boxed",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000007042"
},
"roleDirection": true
},
{
"from": "Table",
"to": "Schema",
"label": "",
"style": "boxed",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000007043"
},
"roleDirection": false
},
{
"from": "Data Attribute",
"to": "Data Entity",
"label": "",
"style": "boxed",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000007047"
},
"roleDirection": false
},
{
"from": "Data Entity",
"to": "Data Model",
"label": "",
"style": "boxed",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000007046"
},
"roleDirection": true
},
{
"from": "Schema",
"to": "Database",
"label": "",
"style": "boxed",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000007024"
},
"roleDirection": false
},
{
"from": "Business Term",
"to": "Data Attribute",
"label": "",
"style": "arrow",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000007038"
},
"roleDirection": true
},
{
"from": "Data Category",
"to": "Data Attribute",
"label": "",
"style": "arrow",
"type": {
"id": "c0e00000-0000-0000-0000-000000007315"
},
"roleDirection": true
},
{
"from": "KPI",
"to": "Data Attribute",
"label": "",
"style": "arrow",
"type": {
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000007200"
},
"roleDirection": true
}
],
"showOverview": false,
"enableFilters": true,
"showLabels": true,
"showFields": true,
"showLegend": true,
"showPreview": true,
"visitStrategy": "directed",
"layout": "FlowContext",
"maxNodeLabelLength": 50,
"maxEdgeLabelLength": 30,
"layoutOptions": {
"compactGroups": false,
"componentArrangementPolicy": "topmost",
"edgeBends": true,
"edgeBundling": true,
"edgeToEdgeDistance": 5,
"minimumLayerDistance": "auto",
"nodeToEdgeDistance": 5,
"orthogonalRouting": true,
"preciseNodeHeightCalculation": true,
"recursiveGroupLayering": true,
"separateLayers": true,
"webWorkers": true,
"nodePlacer": {
"barycenterMode": true,
"breakLongSegments": true,
"groupCompactionStrategy": "none",
"nodeCompaction": false,
"straightenEdges": true
}
}
}For more information on diagram views, go to About JSON syntax for diagram views.
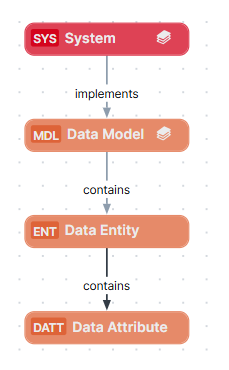
The Data Model asset is the highest level of organizational structure in the semantic layer, and defines the specific structure of data in a System. Data Model assets are related to System and Data Entity assets as follows:
|
Data Model assets are related to... |
Via the relation type... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| System assets | System implements / is implemented in Data Model |
One-to-one relation, whereby:
Note The one-to-one nature of this relationship is what makes Data Models – and, therefore, the entire logical data layer – context-dependent, as opposed to the context-independent conceptual data layer.
|
| Data Entity assets | Data Model contains / is contained in Data Entity |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
A Data Entity represents a real-world object of interest to the business, such as Customer, Employee, or Product. It acts as the abstraction of items in a physical layer and groups a set of related Data Attributes, such as Customer Name and Customer email, to provide a complete definition of that entity.
The Data Entity assets are related to Data Model, Data Domain, and Data Attribute assets as follows:
|
Data Entity assets are related to... |
Via the relation type... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Model assets | Data Entity is part of / contains Data Model |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
| Data Attribute assets | Data Entity contains / is part of Data Attribute |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
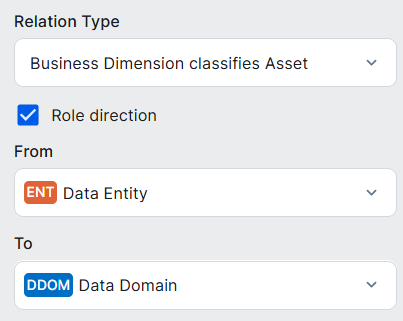
| Data Domain assets |
Business Dimension classifies / is classified by Asset
|
Many-to-many relation, whereby:
|
For other out-of-the-box relations, go to Out-of-the-box relation types.
A Data Attribute is a specific characteristic or property of a Data Entity that represents a single piece of information, such as Email Address, Order Status, or Unit Price. It serves as an abstraction for columns in the physical layer and provides a clear business name and definition. As such, it is a bridge between the physical layer and governance assets.
The Data Attribute assets are related to Data Entity and Data Concept assets as follows:
|
Data Attribute assets are related to... |
Via the relation type... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Entity assets | Data Entity contains / is part of Data Attribute |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
| Data Concept assets | Data Concept classifies / is classified by Data Attribute |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
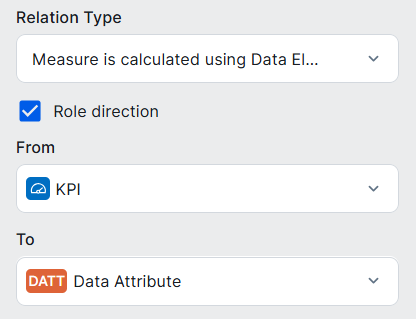
| KPI assets |
Measure is calculated using / is used to calculate by Data Element
|
|
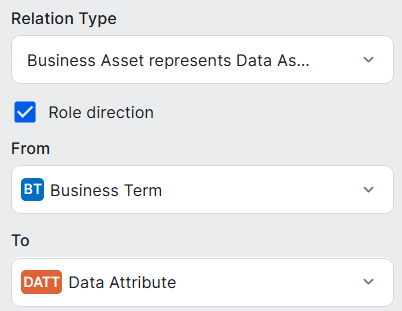
| Business Term assets |
Business asset represents / is represented by Data asset
|
For other out-of-the-box relations, go to Out-of-the-box relation types.
Tip Collibra offers several feature to help you create the semantic layer. For information, go to About the Semantic Layer submenu in Stewardship
About the conceptual layer
The conceptual layer is the highest level of organization in the Guided Stewardship operating model. It represents the overarching, context-independent data structures within an organization’s data landscape. It is where you can define concepts, such as Customer and Product, and their component fields, without direct reference to system-specific implementations.
The conceptual layer is closely related to the semantic layer. The main difference between them is that the conceptual layer is context-independent, whereas the semantic layer describes the structure in an individual System. The definition of the conceptual layer can be very useful for larger organizations that have data governance experience. For other organizations, defining the physical layer and the semantic layer can be a good starting point. If the full Guided Stewardship operating model is too complex for your organization, we advise to focus on the semantic layer because the semantic layer provides better out-of-the-box features and relation possibilities to the physical layer.
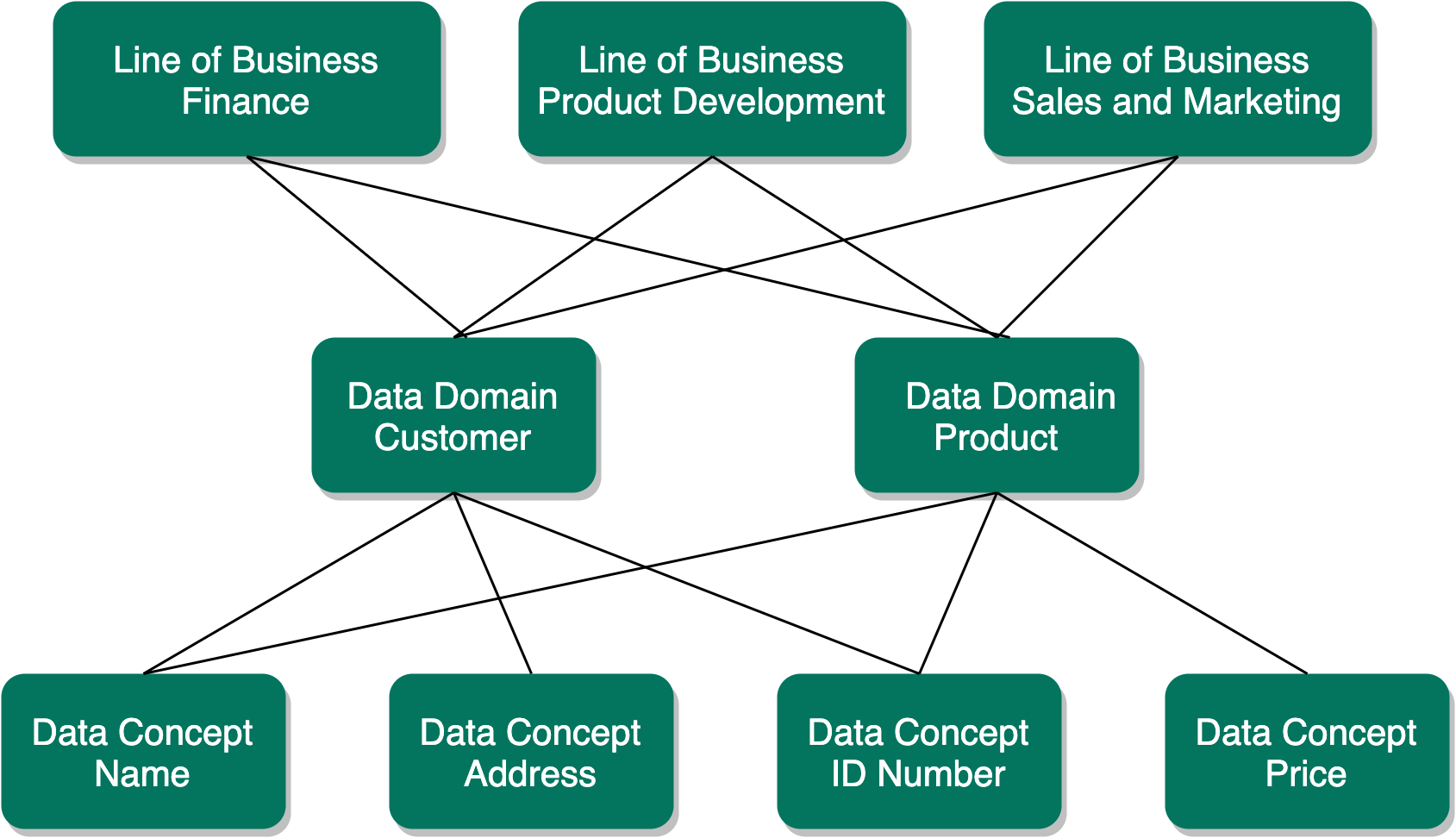
The organization of the conceptual layer is based on many-to-many relationships, which makes the conceptual layer more concise and flexible than tree-like arrangements that rely strictly on one-to-one and one-to-many relationships.
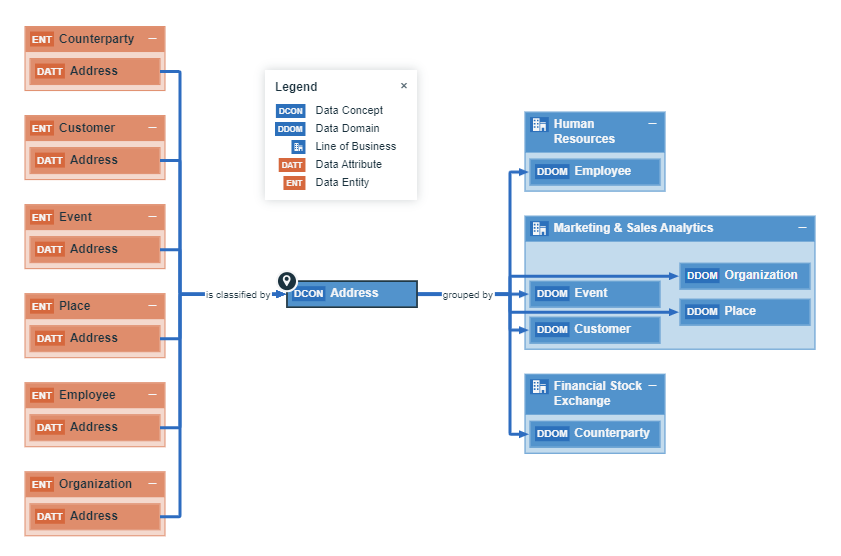
In this next example, the Data Attribute Address is used in several Data Entities, such as Customer Address, Event Address and Employee Address.
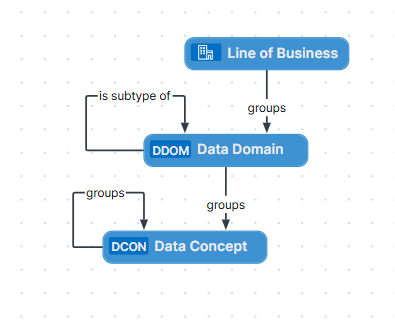
The Line of Business asset type is the highest level of abstraction in the conceptual layer. Also known as business unit or business area, it represents a specific area of business in an organization.
Example Finance, Sales, Retail, Investment Management
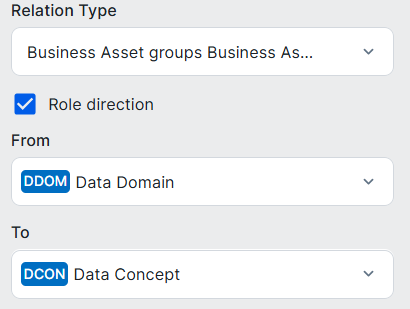
Line of Business assets are related to Data Domain assets as follows:
|
Line of business assets are related to... |
Via the relation type... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
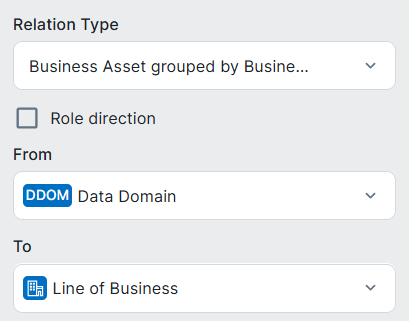
| Data Domain assets |
Business Asset groups / is grouped by Business Asset
|
Many-to-many relation, whereby:
|
Data domains, also known as data categories or subject areas, are high-level, theoretical representations of your data in the conceptual layer. They represent the structure of concepts in data environments and contain all the different nuances of corresponding business terms.
Example Customer, Employee, User, Order, Product
Data Domain assets are related to Line of Business assets, Data Concept, and other Data Domain as follows:
|
Data Domain assets are related to... |
Via the relation type... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Line of Business assets |
Business Asset groups / is grouped by Business Asset
|
Many-to-many relation, whereby:
|
| Data Concept assets |
Business Asset groups / is grouped by Business Asset
|
Many-to-many relation, whereby:
|
|
Other Data Domain assets |
Data Domain has subtype / is subtype of Data Domain |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
A Data Concept asset is a high-level theoretical representation of your data and describes one aspect of one or more data domains.
Example Address, Name, ID number, Phone number, Price, Year
Data Concept assets represent the most common concepts that are used to organize database content.
They are the most granular level of context-independent structure users can establish within the conceptual layer. Data Concept assets are comparable to columns in the physical layer and Data Entity assets in the semantic layer.
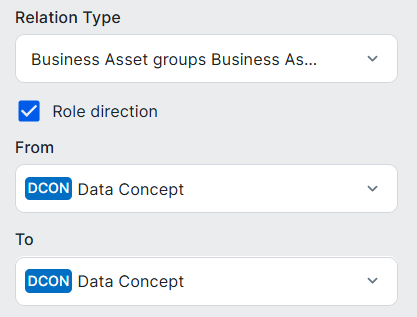
Data Concept assets are related to Data Domain, other Data Concept, and Data Attribute assets.
|
Data Concept assets are related to... |
Via the relation type... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Domain assets |
Business Asset groups / grouped by Business Asset
|
Many-to-many relation, whereby:
|
|
Other Data Concept assets |
Business Asset groups / grouped by Business Asset
|
Many-to-many relation, whereby:
|
| Data Attribute assets |
Data Concept classifies / is classified by Data Attribute |
Many-to-one relation, whereby:
|
Technology assets in the Guided Stewardship operating model
The following Technology assets are considered part of the Guided Stewardship operating system:
- System, which is part of the semantic layer.
- Database, which is part of the physical layer.
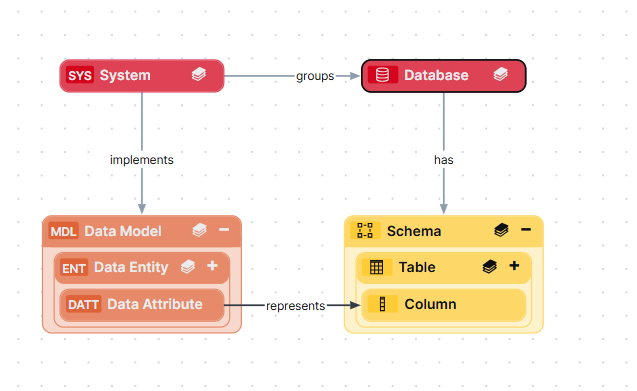
Database assets represent the physical databases in your data environment. They are the highest level of physical data organization in a data environment. Database assets should have specific names, and implement specific technologies, such as PostgreSQL. Although the Database asset type is a Technology asset, it is considered part of the physical layer. Database assets are related to System and Schema assets as follows:
|
Database assets are related to... |
Via the relation type... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| System assets | System groups / is grouped by Database |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
| Schema assets | Database has / belongs to Schema |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|
System assets represent executable software that an organization uses to automate business functions that help run the business smoothly and efficiently. Systems can be any commercially available or privately developed software. Although the System asset type is a Technology Asset, it is considered part of the semantic layer.
Example CRM, ERP, and EDW software
System assets are related to Data Model and Database assets as follows:
|
System assets are related to... |
Via the relation type... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Model assets | System implements / is implemented in Data Model |
One-to-one relation, whereby:
|
| Database assets | System groups / is grouped by Database |
One-to-many relation, whereby:
|